Talos Linux와 OpenTofu를 사용해 Proxmox VE 클러스터 위에 멀티 노드 Kubernetes 클러스터를 부트스트랩하고 업그레이드하는 전체 과정을 정리한다. Cilium, Sealed Secrets, Proxmox CSI 플러그인, 볼륨 프로비저닝까지 다룬다.
Talos는 Kubernetes만 실행하도록 설계된 불변(immutable) 운영체제다. Talos의 장점은 기본으로 제공되는 Kubernetes 설치, 더 작은 공격 면적, 그리고 더 쉬운 유지보수다.
이 글에서는 Proxmox Virtual Environment 8.2 클러스터에 VM으로 실행되는 멀티 노드 Talos 클러스터를 어떻게 부트스트랩하고, 인플레이스 업그레이드까지 할 수 있는지 살펴본다. 이를 위해 IaC 원칙을 따르며 선언적으로 구성할 수 있는 OpenTofu/Terraform을 사용한다.
이 글은 이전에 썼던 Bootstrapping k3s with Cilium과 Debian 12 위에서 Proxmox에 Kubernetes를 올리는 방법의 연장선으로 볼 수 있다. 이전 글들에는 여기서 부족한 설명을 채워줄 보다 너디한 세부사항들이 담겨 있다.
초기 아이디어는 Olav가 작성한 이 글에서 영감을 받았다. 그 글은 훨씬 직설적이고 요약적이다. 나는 거기에 나만의 비틀기와 수정, 생각을 더했는데, 그것들이 이 글을 따로 쓸 가치가 있기를 바란다.
오늘 부트스트랩해 볼 Kubernetes–Tofu 레시피는 Cilium의 eBPF 꿀로 달콤하게 간을 맞추고, Sealed Secrets 소스로 은은히 양념한 뒤, Proxmox CSI Plugin이 프로비저닝하는 볼륨과 함께 256 GiB에서 구워낸다. 옵션 토핑으로는 Quick Sync Video를 지원하기 위한 Intel iGPU 드라이버를 올려 볼 수 있다.
이 Tofu 요리의 핵심 재료는 bpg/proxmox와 siderolabs/talos 프로바이더다. 선택적인 부트스트랩 작업을 완성하기 위해 Mastercard/rastapi와 hashicorp/kubernetes 프로바이더도 활용한다.
마지막에는 Talos-Kubernetes 컨트롤 플레인 노드 3개와 워커 노드 1개를 하나의 클러스터로 묶은 구성을 얻게 된다. 필요에 따라 레시피를 조절하면 된다.
먼저 Talos Linux Image Factory를 둘러보며 필요한 시스템 컴포넌트를 포함한 이미지를 생성한다. 그다음 가상 머신을 Proxmox에 만들고, Talos 머신 설정(machine configuration)을 사용해 Kubernetes 클러스터를 부트스트랩한다.
Kubernetes를 킥스타트한 다음에는 이 설정을 이용해 클러스터를 인플레이스로 업그레이드하는 방법을 살펴보고, 이런 접근 방식에서 더 나아갈 수 있는 개선점을 논의한다.
글이 꽤 길기 때문에, 여기서 사용할 리소스들의 폴더 구조를 먼저 보는 것이 도움이 될 수 있다.
🗃️
├── 📂 talos # Talos 설정
│ ├── 📁 image # Image schematic
│ ├── 📁 inline-manifests # 부트스트랩 매니페스트(Cilium)
│ └── 📁 machine-config # 머신 설정 템플릿
└── 📂 bootstrap # 선택적 부트스트랩
├── 📂 sealed-secrets # 시크릿 관리
│ └── 📁 certificate # 암복호화 키
├── 📂 proxmox-csi-plugin # CSI 드라이버
└── 📂 volumes # 볼륨 프로비저닝
├── 📁 persistent-volume # Kubernetes PV
└── 📁 proxmox-volume # Proxmox 디스크 이미지모든 파일의 전체 목록은 글 뒷부분의 Summary나, 이 글의 리포지토리 여기에서 확인할 수 있다.
이 글에서 사용한 하드웨어는 두 대의 Intel N100 기반 미니 PC(애칭은 euclid와 cantor)와, 세 번째 Intel i3-N305 기반 머신 abel 한 대다. 모두 32 GB RAM을 탑재했고, Proxmox VE 8.2 클러스터로 묶여 있다.
title: Overview of the Proxmox cluster used in this article
flowchart TB
subgraph cluster["Proxmox Cluster"]
subgraph euclid["euclid"]
vm01["VM: ctrl-01"]
end
subgraph abel["abel"]
vm00["VM: ctrl-00"]
vm10["VM: work-00"]
end
subgraph cantor["cantor"]
vm02["VM: ctrl-02"]
end
end
euclid --- abel --- cantor --- euclid클러스터는 Ceph를 사용하면 더 큰 이점을 얻을 수 있지만, 여기서는 다루지 않는다.
Talos가 부팅되고 나면, 제대로 동작하고 클러스터에 참여할 수 있도록 설정해야 한다. talosctl을 사용해 수동 설정도 가능하지만, 여기서는 Talos 프로바이더의 예제를 바탕으로 자동 구성하도록 하겠다.
구성을 한곳에 모으고 중복을 피하기 위해, 클러스터 전체에서 공유하는 값을 담는 cluster 변수 하나를 정의할 수 있다.
variable "cluster" {
description = "Cluster configuration"
type = object({
name = string
endpoint = string
gateway = string
talos_version = string
proxmox_cluster = string
})
}클러스터 이름은 name 변수로 설정한다. endpoint 변수는 주 Kubernetes API 엔드포인트를 의미한다. 고가용성(HA) 구성에서는 로드 밸런서를 사용하는 등, 모든 컨트롤 플레인 노드를 사용하는 방식으로 설정하는 것이 좋다. HA 엔드포인트 구성을 더 알고 싶다면 Talos 문서의 “Decide the Kubernetes Endpoint”를 참고하자.
Sidero Labs는 문서에서 talos_version 선택적 인자를 설정해 두면 업그레이드 시 예기치 못한 동작을 피하는 데 도움이 된다고 권장한다. 여기서도 그 조언을 따른다.
gateway 변수는 모든 노드의 기본 네트워크 게이트웨이를 설정하는 데 사용한다. 조금 앞서 언급하자면, proxmox_cluster 변수는 선택한 CSI 컨트롤러에서 사용할 topology.kubernetes.io/region 레이블을 설정하는 데 사용된다.
이 글에서 사용할 값은 다음과 같다. HA 설정은 건너뛰고, Kubernetes API 엔드포인트를 첫 번째 컨트롤 플레인 노드의 IP로 단순하게 지정했다는 점에 주의하자.
cluster = {
name = "talos"
endpoint = "192.168.1.100"
gateway = "192.168.1.1"
talos_version = "v1.7"
proxmox_cluster = "homelab"
}노드를 쉽게 커스터마이즈할 수 있도록, 필요한 VM을 루프를 돌며 생성·구성하는 데 사용할 맵을 활용하겠다.
variable "nodes" {
description = "Configuration for cluster nodes"
type = map(object({
host_node = string
machine_type = string
datastore_id = optional(string, "local-zfs")
ip = string
mac_address = string
vm_id = number
cpu = number
ram_dedicated = number
update = optional(bool, false)
igpu = optional(bool, false)
}))
}이 맵에서는 hostname을 키로 사용하고, 노드 설정을 값으로 둔다. host_node 변수는 해당 VM이 어느 Proxmox VE 하이퍼바이저 노드에서 실행돼야 하는지 나타낸다. machine_type 변수는 노드 타입을 결정하는데, controlplane 또는 worker 중 하나를 사용한다. 나머지 변수는 VM 설정용이다. 그중 다소 눈에 띄는 것은 datastore_id 변수로, VM 디스크를 저장할 위치를 제어하는 데 사용된다. update 플래그는 어떤 이미지를 사용할지 선택하는 데, igpu 플래그는 호스트 iGPU 패스스루를 활성화하는 데 사용된다.
컨트롤 플레인 노드 3개와 워커 노드 1개로 구성된 4노드 클러스터 설정은 다음과 같다.
nodes = {
"ctrl-00" = {
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.100"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:00"
host_node = "abel"
vm_id = 800
cpu = 8
ram_dedicated = 4096
}
"ctrl-01" = {
host_node = "euclid"
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.101"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:01"
vm_id = 801
cpu = 4
ram_dedicated = 4096
igpu = true
}
"ctrl-02" = {
host_node = "cantor"
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.102"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:02"
vm_id = 802
cpu = 4
ram_dedicated = 4096
}
"work-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "worker"
ip = "192.168.1.110"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:08:00"
vm_id = 810
cpu = 8
ram_dedicated = 4096
igpu = true
}
}여기서는 임의로 euclid와 abel에 호스팅된 ctrl-01과 work-00 노드에만 iGPU 패스스루를 활성화해 두었다.
정의상, 불변 OS는 설치 이후 컴포넌트 변경을 허용하지 않는다. 필요한 모든 것을 하나의 이미지에 다 넣지 않기 위해, Talos를 만든 Sidero Labs는 Talos Linux Image Factory를 만들어, 포함할 패키지를 커스터마이즈할 수 있게 했다.
Talos Linux Image Factory를 사용하면 웹 UI에서 클릭 몇 번으로, 혹은 https://factory.talos.dev/schematics에 YAML/JSON 스키매틱을 POST해 고유한 스키매틱 ID를 받아와 Talos 이미지를 생성할 수 있다.
우리 예제에서는 VM 상태를 Proxmox 하이퍼바이저에 보고하기 위한 QEMU guest agent, Intel microcode, 그리고 Quick Sync Video on Kubernetes를 제대로 활용하기 위한 iGPU 드라이버를 설치하고자 한다.
이 설정을 위한 스키매틱은 다음과 같다.
# tofu/talos/image/schematic.yaml
customization:
systemExtensions:
officialExtensions:
- siderolabs/i915-ucode
- siderolabs/intel-ucode
- siderolabs/qemu-guest-agent이 파일을 https://factory.talos.dev/schematics에 POST하면 다음과 같은 스키매틱 ID를 얻게 된다.
{
"id": "dcac6b92c17d1d8947a0cee5e0e6b6904089aa878c70d66196bb1138dbd05d1a"
}원하는 schematic_id, version, platform, architecture를 조합해, 요청한 이미지를 다운로드할 URL 템플릿은 다음과 같이 만들 수 있다.
https://factory.talos.dev/image/<schematid_id>/<version>/<platform>-<architecture>.raw.gzTalos 이미지를 Proxmox 호스트에 다운로드하는 과정을 자동화하는 단순화된 Tofu 레시피는 다음과 비슷하다.
# tofu/simplified/image.tf
locals {
factory_url = "https://factory.talos.dev"
platform = "nocloud"
arch = "amd64"
version = "v1.7.5"
schematic = file("${path.module}/image/schematic.yaml")
schematic_id = jsondecode(data.http.schematic_id.response_body)["id"]
image_id = "${local.schematic_id}_${local.version}"
}
data "http" "schematic_id" {
url = "${local.factory_url}/schematics"
method = "POST"
request_body = local.schematic
}
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_download_file" "this" {
node_name = "node_name"
content_type = "iso"
datastore_id = "local"
decompression_algorithm = "gz"
overwrite = false
url = "${local.factory_url}/image/${local.schematic_id}/${local.version}/${local.platform}-${local.arch}.raw.gz"
file_name = "talos-${local.schematic_id}-${local.version}-${local.platform}-${local.arch}.img"
}위 설정을 바탕으로, 클러스터 내에서 이미지를 점진적으로 변경할 수 있도록 조금 더 일반화한 레시피를 만들 수 있다.
# tofu/talos/image.tf
locals {
version = var.image.version
schematic = var.image.schematic
schematic_id = jsondecode(data.http.schematic_id.response_body)["id"]
image_id = "${local.schematic_id}_${local.version}"
update_version = coalesce(var.image.update_version, var.image.version)
update_schematic = coalesce(var.image.update_schematic, var.image.schematic)
update_schematic_id = jsondecode(data.http.updated_schematic_id.response_body)["id"]
update_image_id = "${local.update_schematic_id}_${local.update_version}"
}
data "http" "schematic_id" {
url = "${var.image.factory_url}/schematics"
method = "POST"
request_body = local.schematic
}
data "http" "updated_schematic_id" {
url = "${var.image.factory_url}/schematics"
method = "POST"
request_body = local.update_schematic
}
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_download_file" "this" {
for_each = toset(distinct([for k, v in var.nodes : "${v.host_node}_${v.update == true ? local.update_image_id : local.image_id}"]))
node_name = split("_", each.key)[0]
content_type = "iso"
datastore_id = var.image.proxmox_datastore
file_name = "talos-${split("_",each.key)[1]}-${split("_", each.key)[2]}-${var.image.platform}-${var.image.arch}.img"
url = "${var.image.factory_url}/image/${split("_", each.key)[1]}/${split("_", each.key)[2]}/${var.image.platform}-${var.image.arch}.raw.gz"
decompression_algorithm = "gz"
overwrite = false
}여기에 대응하는 변수 정의는 다음과 같다.
variable "image" {
description = "Talos image configuration"
type = object({
factory_url = optional(string, "https://factory.talos.dev")
schematic = string
version = string
update_schematic = optional(string)
update_version = optional(string)
arch = optional(string, "amd64")
platform = optional(string, "nocloud")
proxmox_datastore = optional(string, "local")
})
}여기서는 proxmox_virtual_environment_download_file 리소스의 키를 <host>_<schematic_id>_<version> 형식으로 잡았다. 이렇게 하면 노드의 update 변수가 변경될 때에만 해당 VM이 다시 생성되도록 트리거할 수 있다.
글을 쓰는 시점 기준으로, Talos 프로바이더의 v0.6.0-alpha.1 프리 릴리스에는 스키매틱 ID를 직접 생성해 주는 기능이 포함되어 있다. 그래서 앞으로는 이 단계를 더 단순하게 줄일 수 있을 것이다.
Talos 이미지 커스터마이징에 대한 더 자세한 내용은 Talos Image Factory GitHub 리포지토리 문서를 참고하자.
만약 NVIDIA GPU 가속을 선호한다면, Talos 문서의 NVIDIA GPU 활성화 방법에서 이미 잘 설명하고 있기 때문에 이 글에서 따로 다루지는 않겠다.
Talos 머신 설정의 첫 단계는, 모든 노드가 공유하는 _machine secrets_와 _client configuration_을 생성하는 것이다.
talos_machine_secrets 리소스는 노드 간 보안을 위해 공유할 인증서를 생성한다. 유일한 선택적 인자가 _talos_version_이다.
resource "talos_machine_secrets" "this" {
talos_version = var.cluster.talos_version
}다음으로 talos_client_configuration을 생성하면서 _cluster_name_을 설정하고, 앞에서 만든 머신 시크릿을 추가한다.
data "talos_client_configuration" "this" {
cluster_name = var.cluster.name
client_configuration = talos_machine_secrets.this.client_configuration
nodes = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip]
endpoints = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "controlplane"]
}선택적 설정으로는 모든 _nodes_를 입력 변수에서 추가하고, _endpoints_에는 controlplane 노드만 넣었다. _nodes_와 _endpoints_의 차이에 대해서는 talosctl 문서의 설명을 참고하자.
클라이언트 설정이 준비되었으므로, 이제 Talos 노드용 머신 설정을 준비해야 한다.
여기서는 컨트롤 플레인 노드와 워커 노드용 머신 설정 템플릿을 각각 준비했다. 워커 머신 설정에는 노드 호스트 이름과, 나중에 Proxmox CSI 플러그인이 사용할 표준 topology.kubernetes.io 레이블만 포함된다.
# tofu/talos/machine-config/worker.yaml.tftpl
machine:
network:
hostname: ${hostname}
nodeLabels:
topology.kubernetes.io/region: ${cluster_name}
topology.kubernetes.io/zone: ${node_name}만약 노드가 이리저리 옮겨 다닐 수 있는 고가용성(HA) 구성을 계획 중이라면, 노드 위치에 따라 토폴로지 레이블을 동적으로 설정하는 Talos 또는 Proxmox 클라우드 컨트롤러 매니저를 고려해야 한다.
컨트롤 플레인 머신 설정은 워커와 비슷한 구조로 시작하지만, 컨트롤 플레인 노드에도 스케줄링을 허용하는 클러스터 설정을 추가하고, 기본 kube-proxy를 비활성화한다. 대신 Cilium CNI를 인라인 부트스트랩 매니페스트로 설치할 것이다.
# tofu/talos/machine-config/control-plane.yaml.tftpl
machine:
network:
hostname: ${hostname}
nodeLabels:
topology.kubernetes.io/region: ${cluster_name}
topology.kubernetes.io/zone: ${node_name}
cluster:
allowSchedulingOnControlPlanes: true
network:
cni:
name: none
proxy:
disabled: true
# Optional Gateway API CRDs
extraManifests:
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_gatewayclasses.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/experimental/gateway.networking.k8s.io_gateways.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_httproutes.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_referencegrants.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_grpcroutes.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/experimental/gateway.networking.k8s.io_tlsroutes.yaml
inlineManifests:
- name: cilium-values
contents: |
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cilium-values
namespace: kube-system
data:
values.yaml: |-
${indent(10, cilium_values)}
- name: cilium-bootstrap
contents: |
${indent(6, cilium_install)}부트스트랩 시 적용할 추가 매니페스트를 더 넣을 수도 있다. 예를 들어, Gateway API를 사용할 계획이라면 Gateway API CRD를 넣을 수 있다.
각 노드에 대한 _talos_machine_configuration_은 다음 레시피로 준비한다.
data "talos_machine_configuration" "this" {
for_each = var.nodes
cluster_name = var.cluster.name
cluster_endpoint = var.cluster.endpoint
talos_version = var.cluster.talos_version
machine_type = each.value.machine_type
machine_secrets = talos_machine_secrets.this.machine_secrets
config_patches = each.value.machine_type == "controlplane" ? [
templatefile("${path.module}/machine-config/control-plane.yaml.tftpl", {
hostname = each.key
node_name = each.value.host_node
cluster_name = var.cluster.proxmox_cluster
cilium_values = var.cilium.values
cilium_install = var.cilium.install
})
] : [
templatefile("${path.module}/machine-config/worker.yaml.tftpl", {
hostname = each.key
node_name = each.value.host_node
cluster_name = var.cluster.proxmox_cluster
})
]
}cilium-bootstrap _inlineManifest_는 Talos 문서의 잡(Job)을 이용한 Cilium CNI 배포 예제를 수정해, cilium-values inlineManifest ConfigMap에서 전달되는 values를 사용하도록 변경한 것이다. 덕분에 나중에 재사용할 values.yaml 파일 하나로 Cilium을 손쉽게 부트스트랩할 수 있다.
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cilium-install
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cilium-install
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: cilium-install
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: cilium-install
namespace: kube-system
spec:
backoffLimit: 10
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cilium-install
spec:
restartPolicy: OnFailure
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
- effect: PreferNoSchedule
operator: Exists
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
effect: NoExecute
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
effect: PreferNoSchedule
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
serviceAccountName: cilium-install
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- name: cilium-install
image: quay.io/cilium/cilium-cli-ci:latest
env:
- name: KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT
value: "6443"
volumeMounts:
- name: values
mountPath: /root/app/values.yaml
subPath: values.yaml
command:
- cilium
- install
- --version=v1.16.0
- --set
- kubeProxyReplacement=true
- --values
- /root/app/values.yaml
volumes:
- name: values
configMap:
name: cilium-valuesTalos 문서에서 제안하는, Talos와 호환되는 기본 values.yaml 구성은 다음과 같다.
kubeProxyReplacement: true
# Talos specific
# https://www.talos.dev/latest/kubernetes-guides/configuration/kubeprism/
k8sServiceHost: localhost
k8sServicePort: 7445
securityContext:
capabilities:
ciliumAgent: [ CHOWN,KILL,NET_ADMIN,NET_RAW,IPC_LOCK,SYS_ADMIN,SYS_RESOURCE,DAC_OVERRIDE,FOWNER,SETGID,SETUID ]
cleanCiliumState: [ NET_ADMIN,SYS_ADMIN,SYS_RESOURCE ]
cgroup:
autoMount:
enabled: false
hostRoot: /sys/fs/cgroup
# https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/concepts/ipam/
ipam:
mode: kubernetes이 설정은 나중에 L2 Announcements, IngressController, Gateway API, Hubble 등을 선택적으로 활성화하면서 확장할 수 있다. 글의 summary 부분에서 그런 예시를 볼 수 있다.
Cilium의 기능을 더 알고 싶다면, 이전 글 Migrating from MetalLB to Cilium에서 ARP, L2 announcements, LB IPAM 등에 대해 다루었다. 또한 Cilium Gateway API 구현을 Ingress API 대체로 사용하는 방법에 대해서도 별도 글을 썼다.
머신 설정을 적용하려면 먼저 이 설정을 적용할 VM을 생성해야 한다.
Proxmox나 가상 머신이 처음이라면, 이전 글 Kubernetes on Proxmox에서 여러 설정 선택과 PCI 패스스루에 대해 설명해 두었다.
여기서 사용할 proxmox_virtual_environment_vm 레시피는 비교적 직관적이다. 다만 업데이트된 이미지를 사용할지 여부에 따라 달라지는 부트 디스크의 file_id와, 조건부 PCI 패스스루를 위한 dynamic hostpci 블록 정도만 주의하면 된다.
# tofu/talos/virtual-machines.tf
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_vm" "this" {
for_each = var.nodes
node_name = each.value.host_node
name = each.key
description = each.value.machine_type == "controlplane" ? "Talos Control Plane" : "Talos Worker"
tags = each.value.machine_type == "controlplane" ? ["k8s", "control-plane"] : ["k8s", "worker"]
on_boot = true
vm_id = each.value.vm_id
machine = "q35"
scsi_hardware = "virtio-scsi-single"
bios = "seabios"
agent {
enabled = true
}
cpu {
cores = each.value.cpu
type = "host"
}
memory {
dedicated = each.value.ram_dedicated
}
network_device {
bridge = "vmbr0"
mac_address = each.value.mac_address
}
disk {
datastore_id = each.value.datastore_id
interface = "scsi0"
iothread = true
cache = "writethrough"
discard = "on"
ssd = true
file_format = "raw"
size = 20
file_id = proxmox_virtual_environment_download_file.this["${each.value.host_node}_${each.value.update == true ? local.update_image_id : local.image_id}"].id
}
boot_order = ["scsi0"]
operating_system {
type = "l26" # Linux Kernel 2.6 - 6.X.
}
initialization {
datastore_id = each.value.datastore_id
ip_config {
ipv4 {
address = "${each.value.ip}/24"
gateway = var.cluster.gateway
}
}
}
dynamic "hostpci" {
for_each = each.value.igpu ? [1] : []
content {
# Passthrough iGPU
device = "hostpci0"
mapping = "iGPU"
pcie = true
rombar = true
xvga = false
}
}
}iGPU를 사용하려면 먼저 Proxmox에서 매핑을 해둬야 한다. 이는 Datacenter > Resource Mappings > Add 메뉴에서 가능하다. 모든 물리 노드를 하나씩 확인하면서, 각 노드에서 사용 가능한 iGPU를 아래 그림처럼 수동으로 매핑해 준다.
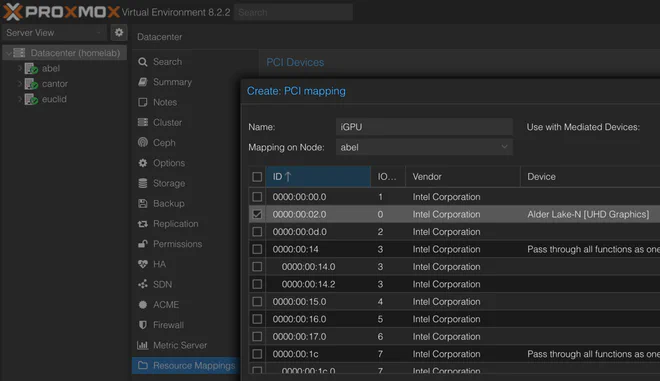
Proxmox Datacenter Resource Mapping (원본 보기)
VM이 부팅되고 나면, 이름 그대로인 talos_machine_configuration_apply 리소스를 사용해 Talos 머신 설정을 적용할 수 있다.
resource "talos_machine_configuration_apply" "this" {
depends_on = [proxmox_virtual_environment_vm.this]
for_each = var.nodes
node = each.value.ip
client_configuration = talos_machine_secrets.this.client_configuration
machine_configuration_input = data.talos_machine_configuration.this[each.key].machine_configuration
lifecycle {
replace_triggered_by = [proxmox_virtual_environment_vm.this[each.key]]
}
}VM이 올라온 뒤에만 실행되도록 의존성을 걸어 두었다. 또한, 부트 이미지가 바뀌어 업그레이드를 진행할 때처럼 VM이 변경되면 설정도 다시 적용되도록 했다.
마지막으로 talos_machine_bootstrap 리소스를 사용해 클러스터를 부트스트랩할 수 있다.
resource "talos_machine_bootstrap" "this" {
node = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "controlplane"][0]
endpoint = var.cluster.endpoint
client_configuration = talos_machine_secrets.this.client_configuration
}여기서는 단순하게 첫 번째 컨트롤 플레인 노드의 IP를 _node_로 사용했다. 대신 옵션인 클러스터 엔드포인트는 (로드 밸런싱이 되어 있을 수도 있는) 공용 엔드포인트를 넣었다.
클러스터가 제대로 동작하는지 확인하기 위해, 클러스터 헬스를 조회한다.
data "talos_cluster_health" "this" {
depends_on = [
talos_machine_configuration_apply.this,
talos_machine_bootstrap.this
]
client_configuration = data.talos_client_configuration.this.client_configuration
control_plane_nodes = [for k, v in var.cluster_config.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "controlplane"]
worker_nodes = [for k, v in var.cluster_config.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "worker"]
endpoints = data.talos_client_configuration.this.endpoints
timeouts = {
read = "10m"
}
}클러스터가 올라오고 헬시한 상태가 되면, talos_cluster_kubeconfig 데이터 소스를 통해 kubeconfig 파일을 가져올 수 있다.
data "talos_cluster_kubeconfig" "this" {
depends_on = [
talos_machine_bootstrap.this,
data.talos_cluster_health.this
]
node = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "controlplane"][0]
endpoint = var.cluster.endpoint
client_configuration = talos_machine_secrets.this.client_configuration
timeouts = {
read = "1m"
}
}여기에서도 node 파라미터로 첫 번째 컨트롤 플레인 노드 IP를 사용했고, 선택적인 endpoint는 클러스터 엔드포인트로 설정했다.
Talos 모듈은 talosctl 도구에서 사용할 클라이언트 설정 파일과, kubectl에서 사용할 Kubernetes 설정 파일을 출력하도록 구성했다.
# tofu/talos/output.tf
output "client_configuration" {
value = data.talos_client_configuration.this
sensitive = true
}
output "kube_config" {
value = data.talos_cluster_kubeconfig.this
sensitive = true
}
output "machine_config" {
value = data.talos_machine_configuration.this
}디버깅을 위해 머신 설정도 포함했는데, 이것도 엄밀히 말하면 민감 정보로 표시하는 편이 낫다.
클러스터가 올라가고 kubeconfig 파일도 준비되었다면, 이제 클러스터를 부트스트랩하기 시작할 수 있다.
Sealed Secrets는 다음과 같이 약속한다.
[SealedSecret 객체]는 나머지 설정과 함께 로컬 코드 리포지터리에 안전하게 저장할 수 있습니다.
즉, Sealed Secrets는 Secrets Store CSI Driver 같은 대안이 될 수 있고, 이름 그대로 시크릿을 설정과 같은 저장소에 둘 수 있게 해 준다.
이 접근 방식의 단점은 복호화를 위한 키를 반드시 보관해야 한다는 점이다. 클러스터를 한 번 날리고 재구축하는 경우, 기존 SealedSecret 오브젝트를 다시 사용하려면 과거와 동일한 암복호화 키를 주입해야 한다.
이를 위한 초기 시크릿을 부트스트랩하려면 다음과 같은 Tofu 레시피를 사용할 수 있다.
# tofu/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/config.tf
resource "kubernetes_namespace" "sealed-secrets" {
metadata {
name = "sealed-secrets"
}
}
resource "kubernetes_secret" "sealed-secrets-key" {
depends_on = [ kubernetes_namespace.sealed-secrets ]
type = "kubernetes.io/tls"
metadata {
name = "sealed-secrets-bootstrap-key"
namespace = "sealed-secrets"
labels = {
"sealedsecrets.bitnami.com/sealed-secrets-key" = "active"
}
}
data = {
"tls.crt" = var.cert.cert
"tls.key" = var.cert.key
}
}cert 변수는 다음과 같이 정의한다.
# tofu/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/variables.tf
variable "cert" {
description = "Certificate for encryption/decryption"
type = object({
cert = string
key = string
})
}이 설정은 sealed-secrets 네임스페이스를 생성하고, 그 안에 Sealed Secrets가 자동으로 감지할 시크릿 하나를 만든다.
유효한 Sealed Secrets 인증서–키 페어는 OpenSSL로 다음 명령을 실행해 생성할 수 있다.
openssl req -x509 -days 365 -nodes -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout sealed-secrets.key -out sealed-secrets.cert -subj "/CN=sealed-secret/O=sealed-secret"위에서 생성한 cert/key 파일이 앞서 본 cert 변수의 입력으로 사용된다.
보안을 강화하려면 인증서를 주기적으로 교체하고 시크릿을 재암호화하는 것이 좋다.
우리는 Proxmox 위에서 실행 중이므로, CSI(Container Storage Interface) 드라이버로 Proxmox 자체를 활용하는 것이 자연스럽다.
이를 위한 좋은 선택지가 바로 Serge Logvinov가 만든 Proxmox CSI Plugin이다. 이를 통해 Kubernetes 클러스터에 영속 스토리지를 프로비저닝할 수 있다.
Proxmox CSI Plugin 구성 방법은 이전 글 Kubernetes Proxmox CSI에서 다루었기 때문에, 여기서는 간단히만 짚고 넘어가겠다.
먼저 Proxmox에 CSI 역할(role)을 생성해야 한다.
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_role" "csi" {
role_id = "CSI"
privileges = [
"VM.Audit",
"VM.Config.Disk",
"Datastore.Allocate",
"Datastore.AllocateSpace",
"Datastore.Audit"
]
}그리고 이 역할을 kubernetes-csi 사용자에 부여한다.
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_user" "kubernetes-csi" {
user_id = "kubernetes-csi@pve"
comment = "User for Proxmox CSI Plugin"
acl {
path = "/"
propagate = true
role_id = proxmox_virtual_environment_role.csi.role_id
}
}그다음 해당 사용자에게 토큰을 생성한다.
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_user_token" "kubernetes-csi-token" {
comment = "Token for Proxmox CSI Plugin"
token_name = "csi"
user_id = proxmox_virtual_environment_user.kubernetes-csi.user_id
privileges_separation = false
}그리고 Proxmox CSI Plugin 문서에 따라 특권 네임스페이스에 이 정보를 입력해야 한다.
resource "kubernetes_namespace" "csi-proxmox" {
metadata {
name = "csi-proxmox"
labels = {
"pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce" = "privileged"
"pod-security.kubernetes.io/audit" = "baseline"
"pod-security.kubernetes.io/warn" = "baseline"
}
}
}이 네임스페이스에 Proxmox CSI Plugin 설정을 담은 시크릿을 만든다.
resource "kubernetes_secret" "proxmox-csi-plugin" {
metadata {
name = "proxmox-csi-plugin"
namespace = kubernetes_namespace.csi-proxmox.id
}
data = {
"config.yaml" = <<EOF
clusters:
- url: "${var.proxmox.endpoint}/api2/json"
insecure: ${var.proxmox.insecure}
token_id: "${proxmox_virtual_environment_user_token.kubernetes-csi-token.id}"
token_secret: "${element(split("=", proxmox_virtual_environment_user_token.kubernetes-csi-token.value), length(split("=", proxmox_virtual_environment_user_token.kubernetes-csi-token.value)) - 1)}"
region: ${var.proxmox.cluster_name}
EOF
}
}Proxmox CSI Plugin을 이용하면 csi.proxmox.sinextra.dev _provisioner_를 사용하는 StorageClass에 연결된 PersistentVolumeClaim으로 볼륨을 프로비저닝할 수 있다. 예를 들어 다음과 같다.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: pvc-test
namespace: proxmox-csi-test
spec:
storageClassName: proxmox-csi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi이에 대응하는 StorageClass는 다음과 같다.
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass
metadata:
name: proxmox-csi
provisioner: csi.proxmox.sinextra.dev
parameters:
cache: writethrough
csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4
storage: local-zfs이렇게 구성하면 Proxmox에 VM 디스크가 자동으로 생성되고, 해당 VM 디스크를 마운트하는 PersistentVolume가 함께 생성된다. 문제는 생성된 VM 디스크 이름이 vm-9999-pvc-96bff316-1d50-45d5-b8fa-449bb3825211처럼 랜덤 UUID를 포함한다는 점이다. 클러스터를 재구축한 뒤 동일한 디스크를 다시 참조하려면 상당히 번거로워진다.
이 문제의 한 가지 해결책은 Proxmox에서 VM 디스크를 수동으로 만들고, 이를 참조하는 PersistentVolume를 수동으로 만드는 것이다. 여기서는 이 방식으로 진행하겠다.
다만 우리가 사용하는 Proxmox 프로바이더는 (아직) VM 디스크를 직접 생성하는 기능을 지원하지 않는다. 그래서 Proxmox VE REST API를 써야 한다. 이를 위해 Mastercard restapi 프로바이더를 활용해 다음과 같은 OpenTofu 레시피를 작성할 수 있다.
# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/proxmox-volumes/proxmox-volume.tf
locals {
filename = "vm-${var.volume.vmid}-${var.volume.name}"
}
resource "restapi_object" "proxmox-volume" {
path = "/api2/json/nodes/${var.volume.node}/storage/${var.volume.storage}/content/"
id_attribute = "data"
force_new = [var.volume.size]
data = jsonencode({
vmid = var.volume.vmid
filename = local.filename
size = var.volume.size
format = var.volume.format
})
lifecycle {
prevent_destroy = true
}
}
output "node" {
value = var.volume.node
}
output "storage" {
value = var.volume.storage
}
output "filename" {
value = local.filename
}입력 변수 정의는 다음과 같다.
# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/proxmox-volumes/variables.tf
variable "proxmox_api" {
type = object({
endpoint = string
insecure = bool
api_token = string
})
sensitive = true
}
variable "volume" {
type = object({
name = string
node = string
size = string
storage = optional(string, "local-zfs")
vmid = optional(number, 9999)
format = optional(string, "raw")
})
}Kubernetes 쪽에서는 Hashicorp kubernetes 프로바이더를 이용해 대응하는 PersistentVolume를 생성한다.
# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/persistent-volume/config.tf
resource "kubernetes_persistent_volume" "pv" {
metadata {
name = var.volume.name
}
spec {
capacity = {
storage = var.volume.capacity
}
access_modes = var.volume.access_modes
storage_class_name = var.volume.storage_class_name
mount_options = var.volume.mount_options
volume_mode = var.volume.volume_mode
persistent_volume_source {
csi {
driver = var.volume.driver
fs_type = var.volume.fs_type
volume_handle = var.volume.volume_handle
volume_attributes = {
cache = var.volume.cache
ssd = var.volume.ssd == true ? "true" : "false"
storage = var.volume.storage
}
}
}
}
}이 모듈이 받는 변수는 다음과 같다.
# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/persistent-volume/variables.tf
variable "volume" {
description = "Volume configuration"
type = object({
name = string
capacity = string
volume_handle = string
access_modes = optional(list(string), ["ReadWriteOnce"])
storage_class_name = optional(string, "proxmox-csi")
fs_type = optional(string, "ext4")
driver = optional(string, "csi.proxmox.sinextra.dev")
volume_mode = optional(string, "Filesystem")
mount_options = optional(list(string), ["noatime"])
cache = optional(string, "writethrough")
ssd = optional(bool, true)
storage = optional(string, "local-zfs")
})
}Proxmox 볼륨 모듈과 PersistentVolume 모듈을 합치면, 전자의 출력을 후자의 _volume_handle_로 사용해 둘을 연결할 수 있다.
# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/main.tf
module "proxmox-volume" {
for_each = var.volumes
source = "./proxmox-volume"
providers = {
restapi = restapi
}
proxmox_api = var.proxmox_api
volume = {
name = each.key
node = each.value.node
size = each.value.size
storage = each.value.storage
vmid = each.value.vmid
format = each.value.format
}
}
module "persistent-volume" {
for_each = var.volumes
source = "./persistent-volume"
providers = {
kubernetes = kubernetes
}
volume = {
name = each.key
capacity = each.value.size
volume_handle = "${var.proxmox_api.cluster_name}/${module.proxmox-volume[each.key].node}/${module.proxmox-volume[each.key].storage}/${module.proxmox-volume[each.key].filename}"
storage = each.value.storage
}
}이 통합 볼륨 모듈이 받는 입력은 Proxmox API 정보와 볼륨 맵이다.
# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/variables.tf
variable "proxmox_api" {
type = object({
endpoint = string
insecure = bool
api_token = string
cluster_name = string
})
sensitive = true
}
variable "volumes" {
type = map(
object({
node = string
size = string
storage = optional(string, "local-zfs")
vmid = optional(number, 9999)
format = optional(string, "raw")
})
)
}예를 들어, abel 노드에 붙은 4 GB PersistentVolume 하나를 만들고 싶다면, 다음과 같이 입력할 수 있다.
volumes = {
pv-test = {
node = "abel"
size = "4G"
}
}이제 이 PV를 사용하려면, PVC의 volumeName 필드에 해당 PV를 지정하면 된다.
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: lidarr-config
namespace: pvc-test
spec:
storageClassName: proxmox-csi
volumeName: pv-test
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 4G우리는 Ceph, GlusterFS, Longhorn 같은 분산 스토리지를 사용하지 않기 때문에, PVC를 사용하는 파드는 Proxmox 디스크가 붙어 있는 물리 하이퍼바이저 노드에서만 실행되도록 지정해야 한다. 이는 파드의 _nodeSelector_에서 해당 노드의 topology.kubernetes.io/zone 레이블을 참조하는 방식으로 쉽게 지정할 수 있다.
nodeSelector:
topology.kubernetes.io/zone: abel이제 주요 Talos 요리와 일부 곁들임 메뉴까지 준비했으니, 모든 OpenTofu 레시피를 합쳐 하나의 식사 클러스터를 만들어 보자.
전체 작업의 기반이 되는 프로바이더 정의는 다음과 같다.
terraform {
required_providers {
talos = {
source = "siderolabs/talos"
version = "0.5.0"
}
proxmox = {
source = "bpg/proxmox"
version = "0.61.1"
}
kubernetes = {
source = "hashicorp/kubernetes"
version = "2.31.0"
}
restapi = {
source = "Mastercard/restapi"
version = "1.19.1"
}
}
}Proxmox API에 연결하는 정보는 변수로 주입한다.
# tofu/variables.tf
variable "proxmox" {
type = object({
name = string
cluster_name = string
endpoint = string
insecure = bool
username = string
api_token = string
})
sensitive = true
}예를 들어, Proxmox 노드 중 하나에 직접 연결하려면 다음과 같이 변수를 설정할 수 있다.
# tofu/proxmox.auto.tfvars
proxmox = {
name = "abel"
cluster_name = "homelab"
endpoint = "https://192.168.1.10:8006"
insecure = true
username = "root"
api_token = "root@pam!tofu=<UUID>"
}API 토큰은 Datacenter > Permissions > API Tokens 메뉴에서 Add 버튼을 눌러 생성할 수 있다.
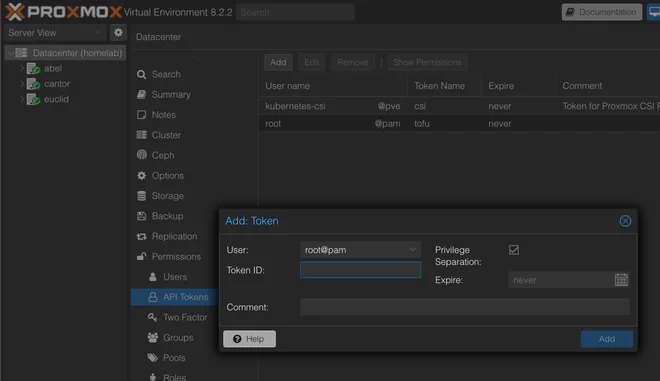
Proxmox API 토큰 생성 (원본 보기)
Talos 프로바이더는 별도 설정이 필요 없고, Proxmox 프로바이더는 앞에서 정의한 변수를 사용한다.
provider "proxmox" {
endpoint = var.proxmox.endpoint
insecure = var.proxmox.insecure
api_token = var.proxmox.api_token
ssh {
agent = true
username = var.proxmox.username
}
}다음으로 Kubernetes 프로바이더는 Talos 모듈의 출력을 사용해 구성한다.
provider "kubernetes" {
host = module.talos.kube_config.kubernetes_client_configuration.host
client_certificate = base64decode(module.talos.kube_config.kubernetes_client_configuration.client_certificate)
client_key = base64decode(module.talos.kube_config.kubernetes_client_configuration.client_key)
cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(module.talos.kube_config.kubernetes_client_configuration.ca_certificate)
}마지막으로, Rest API 프로바이더는 Proxmox 프로바이더와 같은 변수를 사용한다.
provider "restapi" {
uri = var.proxmox.endpoint
insecure = var.proxmox.insecure
write_returns_object = true
headers = {
"Content-Type" = "application/json"
"Authorization" = "PVEAPIToken=${var.proxmox.api_token}"
}
}프로바이더 구성이 끝났으니, 이제 Talos 모듈 설정을 채우자.
module "talos" {
source = "./talos"
providers = {
proxmox = proxmox
}
image = {
version = "v1.7.5"
schematic = file("${path.module}/talos/image/schematic.yaml")
}
cilium = {
install = file("${path.module}/talos/inline-manifests/cilium-install.yaml")
values = file("${path.module}/../kubernetes/cilium/values.yaml")
}
cluster = {
name = "talos"
endpoint = "192.168.1.100"
gateway = "192.168.1.1"
talos_version = "v1.7"
proxmox_cluster = "homelab"
}
nodes = {
"ctrl-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.100"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:00"
vm_id = 800
cpu = 8
ram_dedicated = 4096
}
"ctrl-01" = {
host_node = "euclid"
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.101"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:01"
vm_id = 801
cpu = 4
ram_dedicated = 4096
igpu = true
}
"ctrl-02" = {
host_node = "cantor"
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.102"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:02"
vm_id = 802
cpu = 4
ram_dedicated = 4096
}
"work-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "worker"
ip = "192.168.1.110"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:08:00"
vm_id = 810
cpu = 8
ram_dedicated = 4096
igpu = true
}
}
}여기서 Talos 이미지 스키매틱은 앞서 Image Factory 섹션에서 언급한 외부 파일을 사용한다. Cilium 설치 스크립트는 Cilium Bootstrap 섹션에서 본 것과 동일하며, values는 Summary 섹션에서 보여 줄 외부 파일에서 읽어온다. 나머지 cluster, nodes 변수는 Talos 모듈 섹션에서 본 4노드 클러스터와 동일하다.
생성된 talos-/kube-config 파일과 머신 구성을 출력하려면 다음 레시피를 사용할 수 있다.
# tofu/output.tf
resource "local_file" "machine_configs" {
for_each = module.talos.machine_config
content = each.value.machine_configuration
filename = "output/talos-machine-config-${each.key}.yaml"
file_permission = "0600"
}
resource "local_file" "talos_config" {
content = module.talos.client_configuration.talos_config
filename = "output/talos-config.yaml"
file_permission = "0600"
}
resource "local_file" "kube_config" {
content = module.talos.kube_config.kubeconfig_raw
filename = "output/kube-config.yaml"
file_permission = "0600"
}
output "kube_config" {
value = module.talos.kube_config.kubeconfig_raw
sensitive = true
}
output "talos_config" {
value = module.talos.client_configuration.talos_config
sensitive = true
}이렇게 하면 결과 파일들이 ./output 하위에 저장되고, 다음 명령으로 내용을 직접 확인할 수도 있다.
tofu output -raw kube_config
tofu output -raw talos_configSealed Secrets 모듈을 사용하기로 했다면, Kubernetes 프로바이더를 전달하고 Sealed Secrets 섹션에서 생성한 인증서를 제공해 설정할 수 있다.
module "sealed_secrets" {
depends_on = [module.talos]
source = "./bootstrap/sealed-secrets"
providers = {
kubernetes = kubernetes
}
cert = {
cert = file("${path.module}/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/certificate/sealed-secrets.cert")
key = file("${path.module}/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/certificate/sealed-secrets.key")
}
}proxmox_csi_plugin 모듈은 proxmox, kubernetes 프로바이더와 메인 모듈에서 사용한 proxmox 변수를 그대로 사용한다.
module "proxmox_csi_plugin" {
depends_on = [module.talos]
source = "./bootstrap/proxmox-csi-plugin"
providers = {
proxmox = proxmox
kubernetes = kubernetes
}
proxmox = var.proxmox
}스토리지를 프로비저닝하려면 volumes 모듈을 사용한다. 여기에는 설정된 restapi, kubernetes 프로바이더를 전달하고, Proxmox API를 사용하기 위해 proxmox 변수를 재사용할 수 있다. 볼륨은 노드와 크기만 필수인 맵으로 제공한다.
module "volumes" {
depends_on = [module.proxmox_csi_plugin]
source = "./bootstrap/volumes"
providers = {
restapi = restapi
kubernetes = kubernetes
}
proxmox_api = var.proxmox
volumes = {
pv-test = {
node = "abel"
size = "4G"
}
}
}기존에 만들어 둔 볼륨을 재사용하고 싶다면(예: 클러스터 재구축 시), 다음과 같이 Tofu 상태에 가져올 수 있다.
먼저 Proxmox VM 디스크부터:
tofu import 'module.volumes.module.proxmox-volume["<VOLUME_NAME>"].restapi_object.proxmox-volume' /api2/json/nodes/<NODE>/storage/<DATASTORE_ID>/content/<DATASTORE_ID>:vm-9999-<VOLUME_NAME>그 다음 Kubernetes PersistentVolume을 가져온다.
tofu import 'module.volumes.module.persistent-volume["<VOLUME_NAME>"].kubernetes_persistent_volume.pv' <VOLUME_NAME>클러스터가 정상적으로 올라가고 kubeconfig 파일이 예상 위치에 있다면, 이제 kubectl get nodes를 실행해 다음과 같은 출력을 확인할 수 있어야 한다.
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
ctrl-00 Ready control-plane 30h v1.30.0
ctrl-01 Ready control-plane 30h v1.30.0
ctrl-02 Ready control-plane 30h v1.30.0
work-00 Ready control-plane 30h v1.30.0이제 OpenTofu 풍미의 갓 구운 Talos Kubernetes 클러스터를 채워 넣을 준비가 되었다.
이를 선언적으로 관리하는 데 널리 쓰이는 도구로는 Flux CD, Argo CD가 있다.
나는 후자를 선택했고, 현재 사용 중인 Argo CD + Kustomize + Helm 조합에 대해 별도 글을 작성했다.
참고용으로, 내 홈랩 설정은 여기에서 볼 수 있다.
Talos는 talosctl 도구를 통해 클러스터 업그레이드를 기본 지원한다. 다만 Talos Terraform 프로바이더에는 아직 이 기능에 대한 직접적인 지원이 없다.
이 한계를 보완하기 위해, Talos 모듈을 각 노드에서 사용하는 이미지를 순차적으로 변경할 수 있도록 구성해 두었다. 다음과 같은 간략한 모듈 설정으로 시작한다고 가정해 보자.
image = {
version = "v1.7.4"
schematic = file("schematic.yaml")
}
nodes = {
"ctrl-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
"ctrl-01" = {
host_node = "euclid"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
"ctrl-02" = {
host_node = "cantor"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
}이 설정으로 kubectl get nodes -o wide를 실행하면 다음과 비슷한 결과를 볼 수 있다.
NAME STATUS ROLES VERSION OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ctrl-00 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.4) 6.6.32-talos containerd://1.7.16
ctrl-01 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.4) 6.6.32-talos containerd://1.7.16
ctrl-02 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.4) 6.6.32-talos containerd://1.7.16여기서 보듯 모든 노드가 Talos v1.7.4 위에서 실행 중이다.
여기에 updated_version = "v1.7.5"(3번째 줄)를 추가하고, ctrl-02 노드에 업데이트 이미지를 사용하라고 지정하는(update = true, 19번째 줄) 식으로 한 노드만 업그레이드할 수 있다.
업그레이드 과정에서 기존 VM을 제거하고 새로 생성하기 때문에, 클러스터의 쿼럼 유지를 위해 한 번에 한 노드씩만 수행해야 한다.
image = {
version = "v1.7.4"
updated_version = "v1.7.5"
schematic = file("schematic.yaml")
}
nodes = {
"ctrl-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
"ctrl-01" = {
host_node = "euclid"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
"ctrl-02" = {
host_node = "cantor"
machine_type = "controlplane"
update = true
}
}이제 ctrl-02 노드를 cordon/drain 한 뒤 tofu apply를 실행하면, 얼마 지나지 않아 다음과 같은 상태를 확인할 수 있을 것이다.
NAME STATUS ROLES VERSION OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ctrl-00 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.4) 6.6.32-talos containerd://1.7.16
ctrl-01 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.4) 6.6.32-talos containerd://1.7.16
ctrl-02 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.5) 6.6.33-talos containerd://1.7.18이는 ctrl-02 노드가 이제 Talos v1.7.5로 업그레이드되었음을 의미한다.
같은 절차를 ctrl-01 노드에도 반복해 보자.
image = {
version = "v1.7.4"
updated_version = "v1.7.5"
schematic = file("schematic.yaml")
}
nodes = {
"ctrl-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
"ctrl-01" = {
host_node = "euclid"
machine_type = "controlplane"
update = true
}
"ctrl-02" = {
host_node = "cantor"
machine_type = "controlplane"
update = true
}
}조금 기다리면, 이제 클러스터 상태는 다음과 비슷해질 것이다.
NAME STATUS ROLES VERSION OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ctrl-00 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.4) 6.6.32-talos containerd://1.7.16
ctrl-01 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.5) 6.6.33-talos containerd://1.7.18
ctrl-02 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.5) 6.6.33-talos containerd://1.7.18이제 ctrl-00만 v1.7.4 버전에 남아 있다.
업그레이드를 마무리하기 위해, 메인 버전을 v1.7.5(2번째 줄)로 변경하고 ctrl-01, ctrl-02의 update 플래그를 제거하면 된다.
image = {
version = "v1.7.5"
schematic = file("schematic.yaml")
}
nodes = {
"ctrl-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
"ctrl-01" = {
host_node = "euclid"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
"ctrl-02" = {
host_node = "cantor"
machine_type = "controlplane"
}
}세 번째로 tofu apply를 성공적으로 실행하고 나면, 모든 노드가 Talos v1.7.5로 업그레이드되고, 커널 및 containerd 버전도 갱신된 상태를 확인할 수 있다.
NAME STATUS ROLES VERSION OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
ctrl-00 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.5) 6.6.33-talos containerd://1.7.18
ctrl-01 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.5) 6.6.33-talos containerd://1.7.18
ctrl-02 Ready control-plane v1.30.0 Talos (v1.7.5) 6.6.33-talos containerd://1.7.18여기서 소개한 레시피는 꽤 복잡하고, 개선 여지가 없는 것도 아니다.
이 글을 쓰면서 떠올렸던 개선 아이디어들을 아래에 정리했다. 의견이나 다른 아이디어가 있다면 언제든지 피드백을 받고 싶다.
Talos 프로바이더 0.6.0 릴리스에서는 Image Factory 지원을 예고하고 있다. 개선점 하나는 현재 우리가 직접 스키매틱 ID를 가져오는 코드를 Sidero Labs가 제공하는 구현으로 바꾸는 것이다.
또 다른 흥미로운 아이디어로는 노드별로 서로 다른 스키매틱을 사용할 수 있게 하는 것이다. 다만 이는 현재의 업그레이드 절차를 더 복잡하게 만들 것이다.
비균질(heterogeneous) 클러스터를 지원하기 위해 노드별로 머신 설정을 오버라이드할 수 있게 하는 기능도 있으면 유용할 수 있다. 다만 현재로서는 꼭 필요하다고 느끼지는 않는다.
또한 머신 설정으로 구성할 수 있는 내용은 훨씬 다양하다. 예를 들어 Bernd Schorgers (bjw-s)가 여기에서 보여준 구성을 참고할 수 있다.
현재 구현은 Proxmox 기본 네트워크 브리지를 사용한다. 개선 방안으로는 Kubernetes 클러스터 전용 서브넷을 만들고, 방화벽 규칙을 구성하는 작업이 있다.
Serge Logvinov가 이 리포지터리에서 이런 작업을 이미 어느 정도 해 둔 것으로 보이니, 자세히 살펴볼 만하다.
로드 밸런싱과 IPv6 지원도 도입해 볼 만한 흥미로운 주제다.
분산 스토리지로 Ceph를 도입하면, 파드를 특정 물리 하이퍼바이저 노드에 묶지 않고도 동작하게 할 수 있다. 또한 노드가 응답하지 않는 상황에서 페일오버를 구현할 수도 있을 것이다.
또 다른 개선 방향은 Proxmox 프로바이더에 VM 디스크를 직접 생성하는 기능 지원을 요청하는 것이다. 그 기능이 추가된다면 Mastercard REST API 프로바이더를 제거하고 의존성을 줄일 수 있으며, 경험도 더 간결해질 것이다.
실제로 나는 Proxmox 프로바이더 메인테이너에게 이 기능을 요청하는 GitHub 이슈를 올려 두었다.
현재처럼 업그레이드를 위해 VM을 파괴(destroy)하고 다시 만드는 방식은 그다지 우아한 방법이 아니다. 이미 존재하는 talosctl 업그레이드 기능을 Terraform 레벨에서 활용해, Talos 문서가 제안하듯이 클러스터를 그레이스풀하게 업그레이드하는 방식이 더 나을 것이다. 이에 대한 GitHub 이슈가 있지만, 이 댓글은 다소 부정적인 전망을 내놓고 있기도 하다.
현재 상태에서는 cluster.talos_version 변수를 변경하면 클러스터 전체가 파괴되고 재생성된다. 예를 들어 v1.7.5에서 v1.8.0으로 업그레이드할 때 이런 동작이 항상 바람직한 것은 아닐 수 있다.
이 글에서 사용한 리소스는 이 사이트 코드를 호스팅하는 GitLab 리포지터리에서 확인할 수 있다.
이 구성으로 돌아가는 내 홈랩 IaC 설정의 스냅샷은 GitHub에 있다.
🗃️
├── 📂 kubernetes
│ └── 📂 cilium
│ ├── 📋 kustomization.yaml
│ ├── 📄 announce.yaml
│ ├── 📄 ip-pool.yaml
│ └── 📄 values.yaml
└── 📂 tofu
├── 📝 providers.tf
├── 📝 variables.tf
├── 📃 proxmox.auto.tfvars
├── 📝 main.tf
├── 📝 output.tf
├── 📂 talos
│ ├── 📝 providers.tf
│ ├── 📝 variables.tf
│ ├── 📝 image.tf
│ ├── 📝 config.tf
│ ├── 📝 virtual-machines.tf
│ ├── 📝 output.tf
│ ├── 📂 image
│ │ └── 📄 schematic.yaml
│ ├── 📂 machine-config
│ │ ├── 📋 control-plane.yaml.tftpl
│ │ └── 📋 worker.yaml.tftpl
│ └── 📂 inline-manifests
│ └── 📄 cilium-install.yaml
└── 📂 bootstrap
├── 📂 sealed-secrets
│ ├── 📝 providers.tf
│ ├── 📝 variables.tf
│ └── 📝 config.tf
├── 📂 proxmox-csi-plugin
│ ├── 📝 providers.tf
│ ├── 📝 variables.tf
│ └── 📝 config.tf
└── 📂 volumes
├── 📂 persistent-volume
│ ├── 📝 providers.tf
│ ├── 📝 variables.tf
│ └── 📝 config.tf
├── 📂 proxmox-volume
│ ├── 📝 providers.tf
│ ├── 📝 variables.tf
│ └── 📝 config.tf
├── 📝 providers.tf
├── 📝 variables.tf
└── 📝 main.tf# tofu/providers.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
talos = {
source = "siderolabs/talos"
version = "0.5.0"
}
proxmox = {
source = "bpg/proxmox"
version = "0.61.1"
}
kubernetes = {
source = "hashicorp/kubernetes"
version = "2.31.0"
}
restapi = {
source = "Mastercard/restapi"
version = "1.19.1"
}
}
}
provider "proxmox" {
endpoint = var.proxmox.endpoint
insecure = var.proxmox.insecure
api_token = var.proxmox.api_token
ssh {
agent = true
username = var.proxmox.username
}
}
provider "kubernetes" {
host = module.talos.kube_config.kubernetes_client_configuration.host
client_certificate = base64decode(module.talos.kube_config.kubernetes_client_configuration.client_certificate)
client_key = base64decode(module.talos.kube_config.kubernetes_client_configuration.client_key)
cluster_ca_certificate = base64decode(module.talos.kube_config.kubernetes_client_configuration.ca_certificate)
}
provider "restapi" {
uri = var.proxmox.endpoint
insecure = var.proxmox.insecure
write_returns_object = true
headers = {
"Content-Type" = "application/json"
"Authorization" = "PVEAPIToken=${var.proxmox.api_token}"
}
}# tofu/variables.tf
variable "proxmox" {
type = object({
name = string
cluster_name = string
endpoint = string
insecure = bool
username = string
api_token = string
})
sensitive = true
}# tofu/proxmox.auto.tfvars
proxmox = {
name = "abel"
cluster_name = "homelab"
endpoint = "https://192.168.1.10:8006"
insecure = true
username = "root"
api_token = "root@pam!tofu=<UUID>"
}# tofu/main.tf
module "talos" {
source = "./talos"
providers = {
proxmox = proxmox
}
image = {
version = "v1.7.5"
schematic = file("${path.module}/talos/image/schematic.yaml")
}
cilium = {
install = file("${path.module}/talos/inline-manifests/cilium-install.yaml")
values = file("${path.module}/../kubernetes/cilium/values.yaml")
}
cluster = {
name = "talos"
endpoint = "192.168.1.100"
gateway = "192.168.1.1"
talos_version = "v1.7"
proxmox_cluster = "homelab"
}
nodes = {
"ctrl-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.100"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:00"
vm_id = 800
cpu = 8
ram_dedicated = 4096
}
"ctrl-01" = {
host_node = "euclid"
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.101"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:01"
vm_id = 801
cpu = 4
ram_dedicated = 4096
igpu = true
}
"ctrl-02" = {
host_node = "cantor"
machine_type = "controlplane"
ip = "192.168.1.102"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:C8:02"
vm_id = 802
cpu = 4
ram_dedicated = 4096
}
"work-00" = {
host_node = "abel"
machine_type = "worker"
ip = "192.168.1.110"
mac_address = "BC:24:11:2E:08:00"
vm_id = 810
cpu = 8
ram_dedicated = 4096
igpu = true
}
}
}
module "sealed_secrets" {
depends_on = [module.talos]
source = "./bootstrap/sealed-secrets"
providers = {
kubernetes = kubernetes
}
cert = {
cert = file("${path.module}/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/certificate/sealed-secrets.cert")
key = file("${path.module}/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/certificate/sealed-secrets.key")
}
}
module "proxmox_csi_plugin" {
depends_on = [module.talos]
source = "./bootstrap/proxmox-csi-plugin"
providers = {
proxmox = proxmox
kubernetes = kubernetes
}
proxmox = var.proxmox
}
module "volumes" {
depends_on = [module.proxmox_csi_plugin]
source = "./bootstrap/volumes"
providers = {
restapi = restapi
kubernetes = kubernetes
}
proxmox_api = var.proxmox
volumes = {
pv-test = {
node = "abel"
size = "4G"
}
}
}# tofu/output.tf
resource "local_file" "machine_configs" {
for_each = module.talos.machine_config
content = each.value.machine_configuration
filename = "output/talos-machine-config-${each.key}.yaml"
file_permission = "0600"
}
resource "local_file" "talos_config" {
content = module.talos.client_configuration.talos_config
filename = "output/talos-config.yaml"
file_permission = "0600"
}
resource "local_file" "kube_config" {
content = module.talos.kube_config.kubeconfig_raw
filename = "output/kube-config.yaml"
file_permission = "0600"
}
output "kube_config" {
value = module.talos.kube_config.kubeconfig_raw
sensitive = true
}
output "talos_config" {
value = module.talos.client_configuration.talos_config
sensitive = true
}# kubernetes/cilium/kustomization.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- announce.yaml
- ip-pool.yaml
helmCharts:
- name: cilium
repo: https://helm.cilium.io
version: 1.16.1
releaseName: "cilium"
includeCRDs: true
namespace: kube-system
valuesFile: values.yaml# kubernetes/cilium/announce.yaml
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2alpha1
kind: CiliumL2AnnouncementPolicy
metadata:
name: default-l2-announcement-policy
namespace: kube-system
spec:
externalIPs: true
loadBalancerIPs: true# kubernetes/cilium/ip-pool.yaml
apiVersion: cilium.io/v2alpha1
kind: CiliumLoadBalancerIPPool
metadata:
name: ip-pool
spec:
blocks:
- start: 192.168.1.220
stop: 192.168.1.255cluster:
name: talos
id: 1
kubeProxyReplacement: true
# Talos specific
k8sServiceHost: localhost
k8sServicePort: 7445
securityContext:
capabilities:
ciliumAgent: [ CHOWN, KILL, NET_ADMIN, NET_RAW, IPC_LOCK, SYS_ADMIN, SYS_RESOURCE, DAC_OVERRIDE, FOWNER, SETGID, SETUID ]
cleanCiliumState: [ NET_ADMIN, SYS_ADMIN, SYS_RESOURCE ]
cgroup:
autoMount:
enabled: false
hostRoot: /sys/fs/cgroup
# https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/concepts/ipam/
ipam:
mode: kubernetes
operator:
rollOutPods: true
resources:
limits:
cpu: 500m
memory: 256Mi
requests:
cpu: 50m
memory: 128Mi
# Roll out cilium agent pods automatically when ConfigMap is updated.
rollOutCiliumPods: true
resources:
limits:
cpu: 1000m
memory: 1Gi
requests:
cpu: 200m
memory: 512Mi
#debug:
# enabled: true
# Increase rate limit when doing L2 announcements
k8sClientRateLimit:
qps: 20
burst: 100
l2announcements:
enabled: true
externalIPs:
enabled: true
enableCiliumEndpointSlice: true
loadBalancer:
# https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/kubernetes/kubeproxy-free/#maglev-consistent-hashing
algorithm: maglev
gatewayAPI:
enabled: true
envoy:
securityContext:
capabilities:
keepCapNetBindService: true
envoy: [ NET_ADMIN, PERFMON, BPF ]
ingressController:
enabled: true
default: true
loadbalancerMode: shared
service:
annotations:
io.cilium/lb-ipam-ips: 192.168.1.223
hubble:
enabled: true
relay:
enabled: true
rollOutPods: true
ui:
enabled: true
rollOutPods: true# tofu/talos/providers.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
proxmox = {
source = "bpg/proxmox"
version = ">=0.60.0"
}
talos = {
source = "siderolabs/talos"
version = ">=0.5.0"
}
}
}# tofu/talos/variables.tf
variable "image" {
description = "Talos image configuration"
type = object({
factory_url = optional(string, "https://factory.talos.dev")
schematic = string
version = string
update_schematic = optional(string)
update_version = optional(string)
arch = optional(string, "amd64")
platform = optional(string, "nocloud")
proxmox_datastore = optional(string, "local")
})
}
variable "cluster" {
description = "Cluster configuration"
type = object({
name = string
endpoint = string
gateway = string
talos_version = string
proxmox_cluster = string
})
}
variable "nodes" {
description = "Configuration for cluster nodes"
type = map(object({
host_node = string
machine_type = string
datastore_id = optional(string, "local-zfs")
ip = string
mac_address = string
vm_id = number
cpu = number
ram_dedicated = number
update = optional(bool, false)
igpu = optional(bool, false)
}))
}
variable "cilium" {
description = "Cilium configuration"
type = object({
values = string
install = string
})
}# tofu/talos/image.tf
locals {
version = var.image.version
schematic = var.image.schematic
schematic_id = jsondecode(data.http.schematic_id.response_body)["id"]
image_id = "${local.schematic_id}_${local.version}"
update_version = coalesce(var.image.update_version, var.image.version)
update_schematic = coalesce(var.image.update_schematic, var.image.schematic)
update_schematic_id = jsondecode(data.http.updated_schematic_id.response_body)["id"]
update_image_id = "${local.update_schematic_id}_${local.update_version}"
}
data "http" "schematic_id" {
url = "${var.image.factory_url}/schematics"
method = "POST"
request_body = local.schematic
}
data "http" "updated_schematic_id" {
url = "${var.image.factory_url}/schematics"
method = "POST"
request_body = local.update_schematic
}
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_download_file" "this" {
for_each = toset(distinct([for k, v in var.nodes : "${v.host_node}_${v.update == true ? local.update_image_id : local.image_id}"]))
node_name = split("_", each.key)[0]
content_type = "iso"
datastore_id = var.image.proxmox_datastore
file_name = "talos-${split("_",each.key)[1]}-${split("_", each.key)[2]}-${var.image.platform}-${var.image.arch}.img"
url = "${var.image.factory_url}/image/${split("_", each.key)[1]}/${split("_", each.key)[2]}/${var.image.platform}-${var.image.arch}.raw.gz"
decompression_algorithm = "gz"
overwrite = false
}# tofu/talos/talos-config.tf
resource "talos_machine_secrets" "this" {
talos_version = var.cluster.talos_version
}
data "talos_client_configuration" "this" {
cluster_name = var.cluster.name
client_configuration = talos_machine_secrets.this.client_configuration
nodes = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip]
endpoints = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "controlplane"]
}
data "talos_machine_configuration" "this" {
for_each = var.nodes
cluster_name = var.cluster.name
cluster_endpoint = "https://${var.cluster.endpoint}:6443"
talos_version = var.cluster.talos_version
machine_type = each.value.machine_type
machine_secrets = talos_machine_secrets.this.machine_secrets
config_patches = each.value.machine_type == "controlplane" ? [
templatefile("${path.module}/machine-config/control-plane.yaml.tftpl", {
hostname = each.key
node_name = each.value.host_node
cluster_name = var.cluster.proxmox_cluster
cilium_values = var.cilium.values
cilium_install = var.cilium.install
})
] : [
templatefile("${path.module}/machine-config/worker.yaml.tftpl", {
hostname = each.key
node_name = each.value.host_node
cluster_name = var.cluster.proxmox_cluster
})
]
}
resource "talos_machine_configuration_apply" "this" {
depends_on = [proxmox_virtual_environment_vm.this]
for_each = var.nodes
node = each.value.ip
client_configuration = talos_machine_secrets.this.client_configuration
machine_configuration_input = data.talos_machine_configuration.this[each.key].machine_configuration
lifecycle {
# re-run config apply if vm changes
replace_triggered_by = [proxmox_virtual_environment_vm.this[each.key]]
}
}
resource "talos_machine_bootstrap" "this" {
node = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "controlplane"][0]
endpoint = var.cluster.endpoint
client_configuration = talos_machine_secrets.this.client_configuration
}
data "talos_cluster_health" "this" {
depends_on = [
talos_machine_configuration_apply.this,
talos_machine_bootstrap.this
]
client_configuration = data.talos_client_configuration.this.client_configuration
control_plane_nodes = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "controlplane"]
worker_nodes = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "worker"]
endpoints = data.talos_client_configuration.this.endpoints
timeouts = {
read = "10m"
}
}
data "talos_cluster_kubeconfig" "this" {
depends_on = [
talos_machine_bootstrap.this,
data.talos_cluster_health.this
]
node = [for k, v in var.nodes : v.ip if v.machine_type == "controlplane"][0]
endpoint = var.cluster.endpoint
client_configuration = talos_machine_secrets.this.client_configuration
timeouts = {
read = "1m"
}
}# tofu/talos/virtual-machines.tf
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_vm" "this" {
for_each = var.nodes
node_name = each.value.host_node
name = each.key
description = each.value.machine_type == "controlplane" ? "Talos Control Plane" : "Talos Worker"
tags = each.value.machine_type == "controlplane" ? ["k8s", "control-plane"] : ["k8s", "worker"]
on_boot = true
vm_id = each.value.vm_id
machine = "q35"
scsi_hardware = "virtio-scsi-single"
bios = "seabios"
agent {
enabled = true
}
cpu {
cores = each.value.cpu
type = "host"
}
memory {
dedicated = each.value.ram_dedicated
}
network_device {
bridge = "vmbr0"
mac_address = each.value.mac_address
}
disk {
datastore_id = each.value.datastore_id
interface = "scsi0"
iothread = true
cache = "writethrough"
discard = "on"
ssd = true
file_format = "raw"
size = 20
file_id = proxmox_virtual_environment_download_file.this["${each.value.host_node}_${each.value.update == true ? local.update_image_id : local.image_id}"].id
}
boot_order = ["scsi0"]
operating_system {
type = "l26" # Linux Kernel 2.6 - 6.X.
}
initialization {
datastore_id = each.value.datastore_id
ip_config {
ipv4 {
address = "${each.value.ip}/24"
gateway = var.cluster.gateway
}
}
}
dynamic "hostpci" {
for_each = each.value.igpu ? [1] : []
content {
# Passthrough iGPU
device = "hostpci0"
mapping = "iGPU"
pcie = true
rombar = true
xvga = false
}
}
}# tofu/talos/output.tf
output "client_configuration" {
value = data.talos_client_configuration.this
sensitive = true
}
output "kube_config" {
value = data.talos_cluster_kubeconfig.this
sensitive = true
}
output "machine_config" {
value = data.talos_machine_configuration.this
}# tofu/talos/image/schematic.yaml
customization:
systemExtensions:
officialExtensions:
- siderolabs/i915-ucode
- siderolabs/intel-ucode
- siderolabs/qemu-guest-agent# tofu/talos/machine-config/control-plane.yaml.tftpl
machine:
network:
hostname: ${hostname}
nodeLabels:
topology.kubernetes.io/region: ${cluster_name}
topology.kubernetes.io/zone: ${node_name}
cluster:
allowSchedulingOnControlPlanes: true
network:
cni:
name: none
proxy:
disabled: true
# Optional Gateway API CRDs
extraManifests:
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_gatewayclasses.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/experimental/gateway.networking.k8s.io_gateways.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_httproutes.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_referencegrants.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/standard/gateway.networking.k8s.io_grpcroutes.yaml
- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/v1.1.0/config/crd/experimental/gateway.networking.k8s.io_tlsroutes.yaml
inlineManifests:
- name: cilium-values
contents: |
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cilium-values
namespace: kube-system
data:
values.yaml: |-
${indent(10, cilium_values)}
- name: cilium-bootstrap
contents: |
${indent(6, cilium_install)}# tofu/talos/machine-config/worker.yaml.tftpl
machine:
network:
hostname: ${hostname}
nodeLabels:
topology.kubernetes.io/region: ${cluster_name}
topology.kubernetes.io/zone: ${node_name}---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cilium-install
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cilium-install
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: cilium-install
namespace: kube-system
---
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: cilium-install
namespace: kube-system
spec:
backoffLimit: 10
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: cilium-install
spec:
restartPolicy: OnFailure
tolerations:
- operator: Exists
- effect: NoSchedule
operator: Exists
- effect: NoExecute
operator: Exists
- effect: PreferNoSchedule
operator: Exists
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
effect: NoSchedule
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
effect: NoExecute
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
effect: PreferNoSchedule
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane
operator: Exists
serviceAccountName: cilium-install
hostNetwork: true
containers:
- name: cilium-install
image: quay.io/cilium/cilium-cli-ci:latest
env:
- name: KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: status.podIP
- name: KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT
value: "6443"
volumeMounts:
- name: values
mountPath: /root/app/values.yaml
subPath: values.yaml
command:
- cilium
- install
- --version=v1.16.0
- --set
- kubeProxyReplacement=true
- --values
- /root/app/values.yaml
volumes:
- name: values
configMap:
name: cilium-values# tofu/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/providers.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
kubernetes = {
source = "hashicorp/kubernetes"
version = ">=2.31.0"
}
}
}# tofu/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/variables.tf
variable "cert" {
description = "Certificate for encryption/decryption"
type = object({
cert = string
key = string
})
}# tofu/bootstrap/sealed-secrets/config.tf
resource "kubernetes_namespace" "sealed-secrets" {
metadata {
name = "sealed-secrets"
}
}
resource "kubernetes_secret" "sealed-secrets-key" {
depends_on = [ kubernetes_namespace.sealed-secrets ]
type = "kubernetes.io/tls"
metadata {
name = "sealed-secrets-bootstrap-key"
namespace = "sealed-secrets"
labels = {
"sealedsecrets.bitnami.com/sealed-secrets-key" = "active"
}
}
data = {
"tls.crt" = var.cert.cert
"tls.key" = var.cert.key
}
}# tofu/bootstrap/proxmox-csi-plugin/providers.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
kubernetes = {
source = "hashicorp/kubernetes"
version = ">=2.31.0"
}
proxmox = {
source = "bpg/proxmox"
version = ">=0.60.0"
}
}
}# tofu/bootstrap/proxmox-csi-plugin/variables.tf
variable "proxmox" {
type = object({
cluster_name = string
endpoint = string
insecure = bool
})
}# tofu/bootstrap/proxmox-csi-plugin/config.tf
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_role" "csi" {
role_id = "CSI"
privileges = [
"VM.Audit",
"VM.Config.Disk",
"Datastore.Allocate",
"Datastore.AllocateSpace",
"Datastore.Audit"
]
}
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_user" "kubernetes-csi" {
user_id = "kubernetes-csi@pve"
comment = "User for Proxmox CSI Plugin"
acl {
path = "/"
propagate = true
role_id = proxmox_virtual_environment_role.csi.role_id
}
}
resource "proxmox_virtual_environment_user_token" "kubernetes-csi-token" {
comment = "Token for Proxmox CSI Plugin"
token_name = "csi"
user_id = proxmox_virtual_environment_user.kubernetes-csi.user_id
privileges_separation = false
}
resource "kubernetes_namespace" "csi-proxmox" {
metadata {
name = "csi-proxmox"
labels = {
"pod-security.kubernetes.io/enforce" = "privileged"
"pod-security.kubernetes.io/audit" = "baseline"
"pod-security.kubernetes.io/warn" = "baseline"
}
}
}
resource "kubernetes_secret" "proxmox-csi-plugin" {
metadata {
name = "proxmox-csi-plugin"
namespace = kubernetes_namespace.csi-proxmox.id
}
data = {
"config.yaml" = <<EOF
clusters:
- url: "${var.proxmox.endpoint}/api2/json"
insecure: ${var.proxmox.insecure}
token_id: "${proxmox_virtual_environment_user_token.kubernetes-csi-token.id}"
token_secret: "${element(split("=", proxmox_virtual_environment_user_token.kubernetes-csi-token.value), length(split("=", proxmox_virtual_environment_user_token.kubernetes-csi-token.value)) - 1)}"
region: ${var.proxmox.cluster_name}
EOF
}
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/providers.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
kubernetes = {
source = "hashicorp/kubernetes"
version = ">= 2.31.0"
}
restapi = {
source = "Mastercard/restapi"
version = ">= 1.19.1"
}
}
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/variables.tf
variable "proxmox_api" {
type = object({
endpoint = string
insecure = bool
api_token = string
cluster_name = string
})
sensitive = true
}
variable "volumes" {
type = map(
object({
node = string
size = string
storage = optional(string, "local-zfs")
vmid = optional(number, 9999)
format = optional(string, "raw")
})
)
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/main.tf
module "proxmox-volume" {
for_each = var.volumes
source = "./proxmox-volume"
providers = {
restapi = restapi
}
proxmox_api = var.proxmox_api
volume = {
name = each.key
node = each.value.node
size = each.value.size
storage = each.value.storage
vmid = each.value.vmid
format = each.value.format
}
}
module "persistent-volume" {
for_each = var.volumes
source = "./persistent-volume"
providers = {
kubernetes = kubernetes
}
volume = {
name = each.key
capacity = each.value.size
volume_handle = "${var.proxmox_api.cluster_name}/${module.proxmox-volume[each.key].node}/${module.proxmox-volume[each.key].storage}/${module.proxmox-volume[each.key].filename}"
storage = each.value.storage
}
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/proxmox-volumes/providers.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
restapi = {
source = "Mastercard/restapi"
version = ">= 1.19.1"
}
}
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/proxmox-volumes/variables.tf
variable "proxmox_api" {
type = object({
endpoint = string
insecure = bool
api_token = string
})
sensitive = true
}
variable "volume" {
type = object({
name = string
node = string
size = string
storage = optional(string, "local-zfs")
vmid = optional(number, 9999)
format = optional(string, "raw")
})
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/proxmox-volumes/proxmox-volume.tf
locals {
filename = "vm-${var.volume.vmid}-${var.volume.name}"
}
resource "restapi_object" "proxmox-volume" {
path = "/api2/json/nodes/${var.volume.node}/storage/${var.volume.storage}/content/"
id_attribute = "data"
force_new = [var.volume.size]
data = jsonencode({
vmid = var.volume.vmid
filename = local.filename
size = var.volume.size
format = var.volume.format
})
lifecycle {
prevent_destroy = true
}
}
output "node" {
value = var.volume.node
}
output "storage" {
value = var.volume.storage
}
output "filename" {
value = local.filename
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/persistent-volume/providers.tf
terraform {
required_providers {
kubernetes = {
source = "hashicorp/kubernetes"
version = ">= 2.31.0"
}
}
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/persistent-volume/variables.tf
variable "volume" {
description = "Volume configuration"
type = object({
name = string
capacity = string
volume_handle = string
access_modes = optional(list(string), ["ReadWriteOnce"])
storage_class_name = optional(string, "proxmox-csi")
fs_type = optional(string, "ext4")
driver = optional(string, "csi.proxmox.sinextra.dev")
volume_mode = optional(string, "Filesystem")
mount_options = optional(list(string), ["noatime"])
cache = optional(string, "writethrough")
ssd = optional(bool, true)
storage = optional(string, "local-zfs")
})
}# tofu/bootstrap/volumes/persistent-volume/config.tf
resource "kubernetes_persistent_volume" "pv" {
metadata {
name = var.volume.name
}
spec {
capacity = {
storage = var.volume.capacity
}
access_modes = var.volume.access_modes
storage_class_name = var.volume.storage_class_name
mount_options = var.volume.mount_options
volume_mode = var.volume.volume_mode
persistent_volume_source {
csi {
driver = var.volume.driver
fs_type = var.volume.fs_type
volume_handle = var.volume.volume_handle
volume_attributes = {
cache = var.volume.cache
ssd = var.volume.ssd == true ? "true" : "false"
storage = var.volume.storage
}
}
}
}
}