MLIR의 'linalg' 다이얼렉트 개요와 설계 근거, 핵심 변환, 구조화 연산의 상위 수준 의미, 데이터 표현(뷰), 메타데이터/명명 연산, YAML/OpDSL 기반 명명 연산 생성, 그리고 모든 linalg 연산의 사양과 예시를 설명한다.
합리적 배경(Rationale)
핵심 변환 집합
Linalg 연산의 상위 수준 설명
공개 이슈와 설계 대안
연산(Operations)
linalg.abs (linalg::AbsOp)linalg.add (linalg::AddOp)linalg.batch_matmul (linalg::BatchMatmulOp)linalg.batch_matvec (linalg::BatchMatvecOp)linalg.batch_mmt4d (linalg::BatchMmt4DOp)linalg.batch_reduce_matmul (linalg::BatchReduceMatmulOp)linalg.batch_vecmat (linalg::BatchVecmatOp)linalg.broadcast (linalg::BroadcastOp)linalg.ceil (linalg::CeilOp)linalg.contract (linalg::ContractOp)linalg.conv_1d_ncw_fcw (linalg::Conv1DNcwFcwOp)linalg.conv_1d_nwc_wcf (linalg::Conv1DNwcWcfOp)linalg.conv_1d (linalg::Conv1DOp)linalg.conv_2d_nchw_fchw (linalg::Conv2DNchwFchwOp)linalg.conv_2d_nchw_fchw_q (linalg::Conv2DNchwFchwQOp)linalg.conv_2d_ngchw_fgchw (linalg::Conv2DNgchwFgchwOp)linalg.conv_2d_ngchw_gfchw (linalg::Conv2DNgchwGfchwOp)linalg.conv_2d_ngchw_gfchw_q (linalg::Conv2DNgchwGfchwQOp)linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_fhwc (linalg::Conv2DNhwcFhwcOp)linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_fhwc_q (linalg::Conv2DNhwcFhwcQOp)linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_hwcf (linalg::Conv2DNhwcHwcfOp)linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_hwcf_q (linalg::Conv2DNhwcHwcfQOp)linalg.conv_2d_nhwgc_gfhwc (linalg::Conv2DNhwgcGfhwcOp)linalg.conv_2d_nhwgc_gfhwc_q (linalg::Conv2DNhwgcGfhwcQOp)linalg.conv_2d (linalg::Conv2DOp)linalg.conv_3d_ncdhw_fcdhw (linalg::Conv3DNcdhwFcdhwOp)linalg.conv_3d_ndhwc_dhwcf (linalg::Conv3DNdhwcDhwcfOp)linalg.conv_3d_ndhwc_dhwcf_q (linalg::Conv3DNdhwcDhwcfQOp)linalg.conv_3d (linalg::Conv3DOp)linalg.copy (linalg::CopyOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_1d_ncw_cw (linalg::DepthwiseConv1DNcwCwOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_1d_nwc_wc (linalg::DepthwiseConv1DNwcWcOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_1d_nwc_wcm (linalg::DepthwiseConv1DNwcWcmOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nchw_chw (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNchwChwOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nhwc_hwc (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNhwcHwcOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nhwc_hwc_q (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNhwcHwcQOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nhwc_hwcm (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNhwcHwcmOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nhwc_hwcm_q (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNhwcHwcmQOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_3d_ncdhw_cdhw (linalg::DepthwiseConv3DNcdhwCdhwOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_3d_ndhwc_dhwc (linalg::DepthwiseConv3DNdhwcDhwcOp)linalg.depthwise_conv_3d_ndhwc_dhwcm (linalg::DepthwiseConv3DNdhwcDhwcmOp)linalg.div (linalg::DivOp)linalg.div_unsigned (linalg::DivUnsignedOp)linalg.dot (linalg::DotOp)linalg.elementwise (linalg::ElementwiseOp)linalg.erf (linalg::ErfOp)linalg.exp (linalg::ExpOp)linalg.fill (linalg::FillOp)linalg.fill_rng_2d (linalg::FillRng2DOp)linalg.floor (linalg::FloorOp)linalg.generic (linalg::GenericOp)linalg.index (linalg::IndexOp)linalg.pack (linalg::PackOp)linalg.softmax (linalg::SoftmaxOp)linalg.unpack (linalg::UnPackOp)linalg.winograd_filter_transform (linalg::WinogradFilterTransformOp)linalg.winograd_input_transform (linalg::WinogradInputTransformOp)linalg.winograd_output_transform (linalg::WinogradOutputTransformOp)linalg.yield (linalg::YieldOp)linalg.log (linalg::LogOp)linalg.map (linalg::MapOp)linalg.matmul (linalg::MatmulOp)linalg.matvec (linalg::MatvecOp)linalg.max (linalg::MaxOp)linalg.min (linalg::MinOp)linalg.mmt4d (linalg::Mmt4DOp)linalg.mul (linalg::MulOp)linalg.negf (linalg::NegFOp)linalg.pooling_nchw_max (linalg::PoolingNchwMaxOp)linalg.pooling_nchw_sum (linalg::PoolingNchwSumOp)linalg.pooling_ncw_max (linalg::PoolingNcwMaxOp)linalg.pooling_ncw_sum (linalg::PoolingNcwSumOp)linalg.pooling_ndhwc_max (linalg::PoolingNdhwcMaxOp)linalg.pooling_ndhwc_min (linalg::PoolingNdhwcMinOp)linalg.pooling_ndhwc_sum (linalg::PoolingNdhwcSumOp)linalg.pooling_nhwc_max (linalg::PoolingNhwcMaxOp)linalg.pooling_nhwc_max_unsigned (linalg::PoolingNhwcMaxUnsignedOp)linalg.pooling_nhwc_min (linalg::PoolingNhwcMinOp)linalg.pooling_nhwc_min_unsigned (linalg::PoolingNhwcMinUnsignedOp)linalg.pooling_nhwc_sum (linalg::PoolingNhwcSumOp)linalg.pooling_nwc_max (linalg::PoolingNwcMaxOp)linalg.pooling_nwc_max_unsigned (linalg::PoolingNwcMaxUnsignedOp)linalg.pooling_nwc_min (linalg::PoolingNwcMinOp)linalg.pooling_nwc_min_unsigned (linalg::PoolingNwcMinUnsignedOp)linalg.pooling_nwc_sum (linalg::PoolingNwcSumOp)linalg.powf (linalg::PowFOp)linalg.quantized_batch_matmul (linalg::QuantizedBatchMatmulOp)linalg.quantized_matmul (linalg::QuantizedMatmulOp)linalg.reciprocal (linalg::ReciprocalOp)linalg.reduce (linalg::ReduceOp)linalg.round (linalg::RoundOp)linalg.rsqrt (linalg::RsqrtOp)linalg.select (linalg::SelectOp)linalg.sqrt (linalg::SqrtOp)linalg.square (linalg::SquareOp)linalg.sub (linalg::SubOp)linalg.tanh (linalg::TanhOp)linalg.transpose (linalg::TransposeOp)linalg.vecmat (linalg::VecmatOp)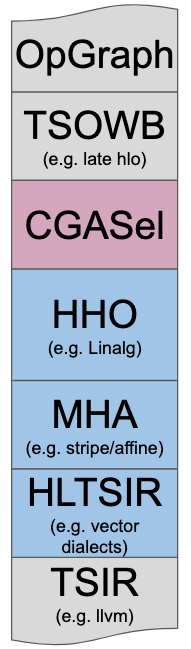 Linalg는 MLIR에서 고수준 계층적 최적화(HHO 상자)를 해결하고, 전문가 컴파일러 혼합(Mixture Of Expert Compilers) 환경(즉, CGSel 상자)과 잘 상호 운용되도록 설계되었다.
Linalg는 MLIR에서 고수준 계층적 최적화(HHO 상자)를 해결하고, 전문가 컴파일러 혼합(Mixture Of Expert Compilers) 환경(즉, CGSel 상자)과 잘 상호 운용되도록 설계되었다.
설계와 아키텍처 결정에 대한 자세한 내용은 Rationale 문서를 참조하라: https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Rationale/RationaleLinalgDialect/
다음의 핵심 변환들은 Linalg 설계를 이끈 중심 요소였다. 이들은 모두 linalg.generic OpInterface의 속성들에 기반하여 구현되며, 하드코딩된 단발성 연산 지식에 의존하는 함정을 피한다.
이들 변환의 텍스트 형태 설명은 향후 작업으로 남아 있지만, Linalg IR에 대해 수행되고 설계에 영향을 준 핵심 변환들을 나열해두는 것은 여전히 유용하다:
Linalg는 앞서 열거된 선행 연구(https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Rationale/RationaleLinalgDialect/#prior-art)에서 적어도 일부 영감을 받았다. 이 설계는 핵심 변환을 가능하게 하는 일반 속성을 갖춘 CustomOps의 정의를 가능하게 하며, 이는 스칼라 load/store 및 기타 연산, 외부 라이브러리 호출과 intrinsic으로의 낮추기를 포함한다.
이들 연산은 입력과 출력 피연산자로 텐서 또는 버퍼 중 하나를 사용할 수 있다. 출력 텐서 피연산자는 통합된 추상화를 제공하고 결과에 형태(shape)를 부여한다. 출력 텐서는 두 가지 형태가 있으며 항상 해당 연산 결과와 연결된다:
“init tensor” 출력 값: 결과를 반복적으로 갱신(“파괴적 갱신”)하여 생성되는 텐서에 대한 초기 값을 제공한다. 이러한 텐서는 항상 어떤 형태로든 물질화된다. 충분한 융합이 발생하면 레지스터 수준의 SSA 값으로만 물질화될 수도 있다. 파괴적 갱신 패턴은 버퍼에 대한 제자리(in-place) 갱신으로 다시 쓸 수 있을 것으로 기대된다(필수는 아님).
“shape-only” 텐서 출력 값: 내부 요소는 페이로드 계산에 사용되지 않고, 더 낮은 수준의 추상화로 형태 정보를 전달하는 용도로만 사용된다. 향후에는 적절한 내장 형태 타입이 제공되면 해당 타입으로 대체될 것이다(자세한 내용은 디스코스 토론 Linalg and Shapes: https://llvm.discourse.group/t/linalg-and-shapes/2421).
Linalg는 텐서와 버퍼에 대한 structured op 추상화를 구현하는 페이로드 보유 연산을 정의한다. 이 linalg.generic 연산은 선택적으로 인덱싱 의미론(루프 인덱스를 linalg.index 연산으로 접근)을 가지는 사용자 정의 연산을 표현할 수 있다. linalg.generic의 속성은 Rationale 문서에 서술된 가이드 원칙을 적용한 결과이다. 각 속성은 간단한 예제와 함께 다음에 열거한다.
linalg.generic 연산은 그 반복 공간 명세를 피연산자들로부터 완전히 도출한다. 이 속성은 국소화된 IR 요소(해당 연산)가 피연산자 타입에 따라 반복에 필요한 제어 흐름을 합성하는 데 필요한 모든 정보를 보유하도록 강제한다. 이러한 IR 국소화 개념은 URUK과 유사성이 있다.
다음은 완전히 명세된 linalg.generic 예시이다. 첫 번째 피연산자는 일반적인 아이덴티티 레이아웃을 갖는 f32 스칼라 요소의 memref이고, 두 번째는 2-stride, 1-offset 레이아웃을 갖는 4-요소 벡터의 memref이다.
// File name: example1.mlir
#accesses = [
affine_map<(m) -> (m)>,
affine_map<(m) -> (m)>
]
#attrs = {
indexing_maps = #accesses,
iterator_types = ["parallel"]
}
func.func @example(%A: memref<?xf32, strided<[1]>>,
%B: memref<?xvector<4xf32>, strided<[2], offset: 1>>) {
linalg.generic #attrs
ins(%A: memref<?xf32, strided<[1]>>)
outs(%B: memref<?xvector<4xf32>, strided<[2], offset: 1>>) {
^bb0(%a: f32, %b: vector<4xf32>):
%c = "some_compute"(%a, %b): (f32, vector<4xf32>) -> (vector<4xf32>)
linalg.yield %c: vector<4xf32>
}
return
}
“입력 및 출력 피연산자가 반복 공간을 정의한다”는 속성은 다음과 유사한 형태로 낮추어 구현된다:
// Run: mlir-opt example1.mlir -allow-unregistered-dialect -convert-linalg-to-loops
// This converted representation is in the `scf` dialect.
// It's syntax can be found here: https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Dialects/SCFDialect/
func.func @example(%arg0: memref<?xf32>,
%arg1: memref<?xvector<4xf32>, strided<[2], offset: 1>>) {
%c0 = arith.constant 0 : index
%c1 = arith.constant 1 : index
%0 = memref.dim %arg0, %c0 : memref<?xf32>
scf.for %arg2 = %c0 to %0 step %c1 {
%1 = memref.load %arg0[%arg2] : memref<?xf32>
%2 = memref.load %arg1[%arg2]
: memref<?xvector<4xf32>, strided<[2], offset: 1>>
%3 = "some_compute"(%1, %2) : (f32, vector<4xf32>) -> vector<4xf32>
memref.store %3, %arg1[%arg2]
: memref<?xvector<4xf32>, strided<[2], offset: 1>>
}
return
}
이 속성은 분석과 변환 단순화에 기여한다. 예를 들어, 동적 피연산자 차원이 서로 일치한다는 전제(assert 런타임 체크의 목적) 하에, 설계상 out-of-bounds 접근이 발생할 수 없음을 보장한다.
루프 형태로 낮추기 전에는 루프 유도 변수와 반복자는 암시적(아직 물질화되지 않음)이다.
주요 함의는 다음과 같다:
MLIR이 동일 IR 안에서 다양한 추상화 수준을 혼합하는 것에 관한 것이므로, 이러한 제한은 실제로 큰 문제가 되지 않는다. Linalg가 점진적으로 다음 추상화 수준으로 낮출 수 있는 한, 적합하지 않은 것들은 우회할 수도 있다.
동시에, 연산 의미를 구조적 데이터 타입에 조건화하는 것은 희소(sparse)와 위치 의존 배열(position-dependent arrays) 및 TACO와 같은 경험이 보여주듯, 비-조밀 텐서로의 확장성 측면에서 매우 유망한 경로이다.
linalg.generic는 반복 공간(즉, 루프)과 데이터 간의 매핑을 정의한다.
다음은 완전히 명세된 예시이다. 첫 번째 memref는 두 차원 모두에 대해 2-stride이고, 두 번째 memref는 아이덴티티 레이아웃을 사용한다.
// File name: example2.mlir
#indexing_maps = [
affine_map<(i, j) -> (j, i)>,
affine_map<(i, j) -> (j)>
]
#attrs = {
indexing_maps = #indexing_maps,
iterator_types = ["parallel", "parallel"]
}
func.func @example(%A: memref<8x?xf32, strided<[2, 2], offset: 0>>,
%B: memref<?xvector<4xf32>>) {
linalg.generic #attrs
ins(%A: memref<8x?xf32, strided<[2, 2], offset: 0>>)
outs(%B: memref<?xvector<4xf32>>) {
^bb0(%a: f32, %b: vector<4xf32>):
%c = "some_compute"(%a, %b): (f32, vector<4xf32>) -> (vector<4xf32>)
linalg.yield %c: vector<4xf32>
}
return
}
“제어 구조와 데이터 구조 간의 가역적 매핑” 속성은 다음과 유사한 형태로 낮추어 구현된다:
// Run: mlir-opt example2.mlir -allow-unregistered-dialect -convert-linalg-to-loops
func.func @example(%arg0: memref<8x?xf32, strided<[2, 2]>>, %arg1: memref<?xvector<4xf32>>) {
%c8 = arith.constant 8 : index
%c0 = arith.constant 0 : index
%c1 = arith.constant 1 : index
%0 = memref.dim %arg0, %c1 : memref<8x?xf32, strided<[2, 2]>>
scf.for %arg2 = %c0 to %0 step %c1 {
scf.for %arg3 = %c0 to %c8 step %c1 {
%1 = memref.load %arg0[%arg3, %arg2] : memref<8x?xf32, strided<[2, 2]>>
%2 = memref.load %arg1[%arg3] : memref<?xvector<4xf32>>
%3 = "some_compute"(%1, %2) : (f32, vector<4xf32>) -> vector<4xf32>
memref.store %3, %arg1[%arg3] : memref<?xvector<4xf32>>
}
}
return
}
이 매핑은 양방향 가능해야 한다. 그 이유는 다음과 같은 질문에 답할 수 있어야 하기 때문이다:
이 두 질문에 답하는 것은 Linalg가 타일링, 타일된 생산자-소비자 융합, 고속 메모리 임시 버퍼로의 승격과 같은 변환을 구현하기 위해 사용하는 주요 분석 중 하나이다.
현재 구현에서는, linalg.generic은 AffineMap의 리스트를 사용한다(앞선 예시들의 #indexing_maps 속성 참조). 이는 실용적인 단기 해결책이며, 장기적으로는 inspector-executor 알고리즘과 유사하게 이 속성을 동적으로 평가할 수도 있다.
linalg.generic 연산은 반복자의 타입을 완전히 선언한다. 이 정보는 변환에서 사용된다.
이들 속성은 해당 분야의 확립된 관행에서 유도되었으며, Ken Kennedy의 "Optimizing Compilers for Modern Architectures"에서의 속성과도 상응한다. Kennedy가 표현한 루프 변환의 합법성에 대한 핵심 아이디어는 “모든 의존 벡터의 사전식 순서를 보존해야 한다”이다.
이는 특정 반복자 타입 덕에 루프 수준에서 더 잘 포착된다. 예: parallel, reduction, partition, permutable/monotonic, sequential, dependence distance 등.
이들 타입은 전통적으로 복잡한 의존성 분석의 결과이며, 폴리헤드럴 커뮤니티에서는 “bands”(예: parallel bands, permutable bands 등, ISL 스케줄 트리 용어)로 불렸다.
linalg.generic에서 정보를 선언적으로 지정하면, 더 낮은 수준 정보로부터 유도하기 어렵거나 심지어 불가능한 속성들을 전달할 수 있다. 이 속성들은 변환에 유용한 시점까지 가져가서 사용한 뒤 폐기할 수 있다.
또한 이 속성들은 프론트엔드/사용자가 보장하는 계약으로도 볼 수 있으며, 컴파일러는 이를 활용할 수 있다. 흔한 예는 히스토그램 계산을 지정하기 위한 데이터 의존적 축소 의미론의 사용이다. 프론트엔드가 적절한 원자적 연산이 사용 가능하다는 추가 지식을 가진 경우, 병렬 의미론을 지정하고 계산 영역에서 특수 원자 연산을 사용하는 것이 더 나을 수 있다.
현재 Linalg는 parallel과 reduction 루프에만 명시적으로 사용되지만, 과거 경험에 비추어 이 추상화는 일반화 가능하다.
linalg.generic 연산은 리전 사용 덕분에 완전히 일반적인 계산 페이로드를 갖는다.
리전은 linalg.generic의 텐서 또는 버퍼 피연산자의 스칼라 원소 타입을 인자로 받는다. 유연성과 라이브러리 호출 매칭을 위해, 추가적인 특수 값들이 전달될 수 있다. 예를 들어, linalg.fill 연산은 버퍼와 추가 스칼라 값을 받는다.
현 시점에서는 리전 의미론에 추가 제약이 없다. 이는 리전과 반복자 타입의 교차점에서 다양한 설계 절충을 탐색할 수 있게 하기 위함이다. 특히, 프론트엔드는 리전 내부 연산이 반복자 타입의 의미와 일치하도록 책임을 진다: 리전은 버퍼를 임의로 캡처하고 그 안에 쓸 수 있다. 만약 이것이 병렬 반복자 요구사항과 충돌한다면, 이는 정의되지 않은 동작이다.
이전 예시들에서는 등록되지 않은 함수 "some_compute"로 계산 페이로드를 이미 보였다. 다음 코드 조각은 구체 연산 addf를 사용하면 어떤 결과가 되는지 보여준다:
// File name: example3.mlir
#map = affine_map<(i, j) -> (i, j)>
#attrs = {
indexing_maps = [#map, #map, #map],
iterator_types = ["parallel", "parallel"]
}
func.func @example(%A: memref<?x?xf32>, %B: memref<?x?xf32>, %C: memref<?x?xf32>) {
linalg.generic #attrs
ins(%A, %B: memref<?x?xf32>, memref<?x?xf32>)
outs(%C: memref<?x?xf32>) {
^bb0(%a: f32, %b: f32, %c: f32):
%d = arith.addf %a, %b : f32
linalg.yield %d : f32
}
return
}
이 함수는 기본적으로 두 행렬(%A와 %B)을 원소별로 더해 다른 행렬(%C)에 저장한다.
“계산 페이로드는 리전으로 지정된다”는 속성은 다음과 유사한 형태로 낮추어 구현된다:
func.func @example(%arg0: memref<?x?xf32>, %arg1: memref<?x?xf32>, %arg2: memref<?x?xf32>) {
%c0 = arith.constant 0 : index
%c1 = arith.constant 1 : index
%0 = memref.dim %arg0, %c0 : memref<?x?xf32>
%1 = memref.dim %arg0, %c1 : memref<?x?xf32>
scf.for %arg3 = %c0 to %0 step %c1 {
scf.for %arg4 = %c0 to %1 step %c1 {
%2 = memref.load %arg0[%arg3, %arg4] : memref<?x?xf32>
%3 = memref.load %arg1[%arg3, %arg4] : memref<?x?xf32>
%4 = arith.addf %2, %3 : f32
memref.store %4, %arg2[%arg3, %arg4] : memref<?x?xf32>
}
}
return
}
루프와 더 낮은 수준 구성으로 낮추는 과정에서, inlined call op 제안에서 논의된 것과 유사한 요구사항이 발생한다. 리전 인자와 캡처를 모두 지원하도록 저수준 인프라가 발전한다면 이를 재사용할 수 있을 것으로 기대한다.
linalg.generic 연산은 SymbolAttr를 지정하여 외부 라이브러리 호출로 매핑될 수 있다. 이 추상화 수준에서 중요한 접착제는, 다양한 변환이 적용된 이후에도 외부 라이브러리를 호출하는 데 필요한 구조를 보존하도록 하는 변환을 수행하는 능력이다.
이는 연산 의미의 보존과 ABI 수준 통합에 관련된 고려사항을 포함한다. 외부 라이브러리 호출을 사용할지, 커스텀 ISA를 사용할지 여부와 관계없이, 코드 생성 측면에서는 고정된 세분성을 보존하는 문제가 유사하다.
다음 예시는 library_call="pointwise_add" 속성을 추가로 지정하여 사용할 외부 라이브러리 호출 이름을 명시한다:
// File name: example4.mlir
#indexing_maps = [
affine_map<(i, j) -> (i, j)>,
affine_map<(i, j) -> (i, j)>,
affine_map<(i, j) -> (i, j)>
]
#attrs = {
indexing_maps = #indexing_maps,
iterator_types = ["parallel", "parallel"],
library_call = "pointwise_add"
}
func.func @example(%A: memref<?x?xf32>, %B: memref<?x?xf32>, %C: memref<?x?xf32>) {
linalg.generic #attrs
ins(%A, %B: memref<?x?xf32>, memref<?x?xf32>)
outs(%C: memref<?x?xf32>) {
^bb0(%a: f32, %b: f32, %c: f32):
%d = arith.addf %a, %b : f32
linalg.yield %d : f32
}
return
}
“외부 라이브러리 호출로 매핑” 속성은 다음과 유사한 형태로 낮추어 구현된다:
// Run: mlir-opt example4.mlir -convert-linalg-to-std
func.func @example(%arg0: memref<?x?xf32>, %arg1: memref<?x?xf32>, %arg2: memref<?x?xf32>) {
%0 = memref.cast %arg0 : memref<?x?xf32> to memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>
%1 = memref.cast %arg1 : memref<?x?xf32> to memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>
%2 = memref.cast %arg2 : memref<?x?xf32> to memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>
call @pointwise_add(%0, %1, %2) : (memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>,
memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>, memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>) -> ()
return
}
func.func @pointwise_add(memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>,
memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>,
memref<?x?xf32, strided<[?, ?], offset: ?>>) attributes {llvm.emit_c_interface}
LLVM로 낮추면 다음과 유사해진다:
// Run: mlir-opt example4.mlir -convert-linalg-to-std | mlir-opt -convert-func-to-llvm
// Some generated code are omitted here.
func.func @example(%arg0: !llvm<"float*">, ...) {
...
llvm.call @pointwise_add(...) : (!llvm<"float*">, ...) -> ()
return
}
llvm.func @pointwise_add(%arg0: !llvm<"float*">, ...) attributes {llvm.emit_c_interface} {
...
llvm.call @_mlir_ciface_pointwise_add(%9, %19, %29) : (!llvm."{ float*, float*, i64, [2 x i64], [2 x i64] }*">, !llvm<"{ f32*, f32*, i64, [2 x i64], [2 x i64] }*">, !llvm<"{ float*, float*, i64, [2 x i64], [2 x i64] }
*">) -> ()
llvm.return
}
llvm.func @_mlir_ciface_pointwise_add(!llvm."{ float*, float*, i64, [2 x i64], [2 x i64] }*">, !llvm<"{ f32*, f32*, i64, [2 x i64], [2 x i64] }*">, !llvm<"{ f32*, f32*, i64, [2 x i64], [2 x i64] }*">) attributes {llvm.emit_c_interface}
linalg 다이얼렉트는 BLAS와 유사한 컨벤션을 채택한다. 즉, 빠른 라이브러리 구현으로 오프로딩할 때 입력/출력 데이터에 대한 비소유 포인터를 추가 메타데이터와 함께 전달한다. 이 컨벤션은 MKL, OpenBLAS, BLIS, cuBLAS, cuDNN 등에서도 발견되며, 더 일반적으로는 언어 경계를 넘는 인터페이스(C++/Python 등)에서도 사용된다.
일반적으로, linalg는 외부로 링크된 사전 컴파일된 라이브러리 호출에 View 데이터 구조에 대한 비소유 포인터를 전달한다.
핵심 속성이 존재하는 경우 상호 운용성을 확장하는 주제에 대한 진행 중인 논의가 있다: https://llvm.discourse.group/t/lowering-optional-attributes-in-linalg-structuredops-to-standard-dialect/333/3
완전하게 중첩된 루프는 타일링과 라이브러리 호출로의 매핑과 같은 핵심 루프 변환을 가능하게 하는 중요한 형태의 구조이다. 불행히도, 이 구조는 부분 루프 융합과 같은 변환으로 쉽게 깨진다. 그 결과 타일링과 라이브러리 호출 매핑이 더 어려워지거나, 심지어 불가능해진다. Linalg 연산은 완전 중첩성을 일급 속성으로 채택한다: 이 구조는 깨질 수 없고, 설계상 IR에서 운반된다.
linalg.generic 연산은 전체 메모리 영역에 쓰는 완전 중첩 루프 중첩을 표현한다. 이는 리전과 루프 전반에 걸친 구조적 제약이며, 변환 단순화에 핵심임이 입증되었다.
언급할 점 하나는, 불완전 중첩 코드를 완전 중첩 코드로 변환하는 것이 루프 분배와 조건문을 가장 안쪽 루프 수준까지 내리는 방식으로 종종 가능하다는 것이다.
Tensor Comprehensions 경험은 가장 안쪽 제어 흐름 중첩을 강제하는 것이 불(boolean) 배열과 predication으로 데이터 병렬 코드를 작성하는 것과 많이 유사하다는 직관을 주었다. 이러한 트릭은 폴리헤드럴 컴파일러에서 비-어파인 제어를 어파인 계산 의존성으로 변환하는 데에도 사용되어 왔다.
이러한 재작성은 일반 IR에서 자동화할 수 있을지 모르지만, linalg.generic은 현재로서는 단지 의미를 강제한다.
핵심 함의는, Linalg 변환이 끝나면 이 깊은 predication으로의 변환을 되돌려야 한다는 점이다. 반복자와 유도 변수가 물질화된 후(즉, linalg.generic에서 낮춘 이후), 전체 성능은 정규화(canonicalization), 폴딩, 그리고 루프 독립 코드 이동(LICM)의 품질에 크게 영향을 받는다.
더 큰 그림에서, 후기 LICM에 대한 의존은 필요하다고 판단된 위험이었다.
지금까지의 여섯 가지 속성은 linalg.generic 연산의 의미를 정의한다. 실제로 이 모든 의미가 엄밀히 필요한지, 그리고 일부는 핵심 가이드 원칙을 유지하면서도 자동으로 유도될 수 있을지 여부는 열린 질문이다.
현재로서는, 여러 고수준 컴파일러에서 작업하며 쌓인 경험적 증거에 기반해 이들 속성의 조합으로 정착했다. 이를 바탕으로 커뮤니티와 더 많이 교류하면서, 원래 아키텍처에 대해 여러 차례의 논의와 설계 변경이 있을 것으로 예상한다.
현재 구현은 Strided MemRef(일명 View) 추상화를 사용한다. linalg에서는 View라는 이름을 Strided MemRef와 혼용한다. 향후에는 다른 구조적 데이터 타입을 사용하고, 래깅(ragged), 혼합-희소 등 타입을 지원할 것으로 기대한다. 희소와 위치 의존 배열에 대한 기존 LIFT 추상화 경험을 활용할 것이다.
메타데이터를 조작하지만 메모리를 이동시키지 않는 연산들의 집합이다. 이 연산들은 view 피연산자와 추가 속성을 받아 새로운 view를 반환한다. 반환된 view는 일반적으로 피연산자 view와 에일리어스한다. 현재 존재하는 연산들은 다음과 같다:
* `memref.view`,
* `memref.subview`,
* `memref.transpose`.
* `linalg.slice`,
* `linalg.reshape`,
향후 필요에 따라 연산이 추가되며 다음을 포함해야 한다:
* `linalg.tile`,
* `linalg.intersection`,
* `linalg.convex_union`,
* `linalg.difference` (뷰 목록에 대해 동작 필요).
이 추가 연산들은 대규모 분산 스텐실 계산 분야에서 효과가 입증된 추상화와 대응한다.
장기적으로는 Legion 데이터 중심 프로그래밍 모델의 추상화가 전반적으로 매력적이다.
추가로, linalg는 일반적으로 사용되는 소수의 명명 연산을 제공한다:
* `linalg.fill`,
* `linalg.dot`,
* `linalg.matmul`,
* `linalg.conv`.
이 명명 연산은 linalg.generic op 인터페이스를 준수한다. 일반 op 인터페이스만으로 기술한 설명으로부터 명명 연산을 자동 생성하는 선언적 메커니즘을 정의하는 작업이 진행 중이다.
이것이 오늘날 소수의 연산만 존재하는 주된 이유이다: 곧 TableGen으로부터 자동 생성될 것으로 예상한다.
Linalg는 아인슈타인 표기에서 영감을 받은 표기법으로부터 명명 연산을 자동 생성하는 선언적 사양과 생성 도구(mlir-linalg-ods-gen)를 제공한다.
mlir-linalg-ods-gen에서 사용하는 구문과 의미는 개발 중이며, Tensor Comprehensions(TC)에서 차용했지만, Linalg에 더 잘 맞도록 몇 가지 차이가 있다:
id : type(symbolic-affine-expression-list)(예: A : f32(M, N + M))로 지정되며, 각 새로운 심볼은 즉시 발견된다. TC는 일반적인 심볼릭 어파인 식을 허용하지 않는다.std_add<k>)로 지정된다. TC에서는 축소 차원이 추론된다. 피연산자 중 하나가 어떤 식에도 사용되지 않으면, shape-only 피연산자로 간주되며, indexing_map의 결과는 축소 차원이 된다.O(i, j) = std_add<k, l>(...)에서 i(및 j)는 위치 0(및 1)의 어파인 차원으로 인코딩되는 병렬 반복자이며, k(및 l)는 위치 2(및 3)의 어파인 차원으로 인코딩되는 축소 반복자이다.attr( strides: 2xi32) 형식으로 연산에 정의할 수 있으며, strides[0]처럼 comprehension에서 참조할 수 있다. 이러한 속성 사용은 어파인 심볼로 파싱되어 연산 정의와 구현을 생성한다. 구체 연산 인스턴스의 경우, 속성에서의 런타임 상수 값이 어파인 심볼 대체와 indexing map 단순화에 사용된다.이 결정들과 구문은 변화할 수 있다. 특히, 연산 특화 속성, 동적 랭크, 일종의 템플릿, 형태 계산 함수 지정 등이 향후 추가될 수 있다.
현재 시점에서 구문과 의미에 다음 제약이 부과된다:
"""로 감싼 doc 문자열을 명명 연산에 첨부할 수 있다. 요약 한 줄을 먼저 포함하고, 이후 자세한 설명을 포함해야 한다.
다음 사양은 명명된 batchmatmul 연산을 정의하는 데 사용될 수 있다:
def batchmatmul(A: f32(Batch, M, K), B: f32(K, N)) -> (C: f32(Batch, M, N))
"""Batch matrix-multiply operation.
This operation performs batch matrix-multiply over ...
"""
{
C(b, m, n) = std_addf<k>(std_mulf(A(b, m, k), B(k, n)));
}
mlir-linalg-ods-gen -gen-ods-decl=1 호출 시, 다음과 같은 ODS가 생성된다:
def batchmatmulOp : LinalgNamedStructured_Op<"batchmatmul", [
NInputs<2>,
NOutputs<1>,
NamedStructuredOpTrait]> { ... }
mlir-linalg-ods-gen -gen-impl=1 호출 시, 다음과 같은 C++가 생성된다:
std::optional<SmallVector<StringRef, 8>> batchmatmul::referenceIterators() {
return SmallVector<StringRef, 8>{
getParallelIteratorTypeName(),
getParallelIteratorTypeName(),
getParallelIteratorTypeName(),
getReductionIteratorTypeName() };
}
std::optional<SmallVector<AffineMap, 8>> batchmatmul::referenceIndexingMaps() {
MLIRContext *context = getContext();
AffineExpr d0, d1, d2, d3;
bindDims(context, d0, d1, d2, d3);
return SmallVector<AffineMap, 8>{
AffineMap::get(4, 0, {d0, d1, d3}),
AffineMap::get(4, 0, {d3, d2}),
AffineMap::get(4, 0, {d0, d1, d2}) };
}
void batchmatmul::regionBuilder(ArrayRef<BlockArgument> args) {
using namespace edsc;
using namespace intrinsics;
Value _0(args[0]), _1(args[1]), _2(args[2]);
Value _4 = std_mulf(_0, _1);
Value _5 = std_addf(_2, _4);
(linalg_yield(ValueRange{ _5 }));
}
Linalg는 YAML 기반 연산 설명 형식으로부터 명명 연산을 자동 생성하는 선언적 생성 도구(mlir-linalg-ods-yaml-gen)를 제공한다. 이 YAML 기반 설명은 더 높은 수준의 DSL(https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Dialects/Linalg/OpDSL/)에서 생성되며 직접 편집하는 용도가 아니다.
이 기능은 현재 개발 중이며, 준비되면 위 기능을 대체할 예정이다. 스키마의 진실 원천은 mlir-linalg-ods-yaml-gen.cpp의 C++ 클래스 ↔ YAML 매핑 트레이트를 참조하라.
위 문서 대부분은 대략 이 경로에도 적용되며, 마이그레이션이 진행됨에 따라 옮겨질 것이다.
여러 공개 이슈와 설계 대안이 진행 중이며, 커뮤니티가 논의하고 검토할 시점이다:
linalg.generic이 네스팅을 지원해야 하는가?linalg.generic 리전이 뷰를 받아야 하는가, 아니면 스칼라만 받아야 하는가?이 핵심 질문들은 MLIR의 일반 맥락, 즉 서로 다른 IR 수준이 원활히 상호 운용되는 맥락에서 생각되어야 한다. 실제로 모든 문제를 동일 IR에서 해결하려는 것은 필요하지도 유익하지도 않을 수 있다.
linalg.abs (linalg::AbsOp)원소별로 abs(x)를 적용.
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): AttrSizedOperandSegments, RecursiveMemoryEffects, SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>, SingleBlock
인터페이스(Interfaces): ConditionallySpeculatable, DestinationStyleOpInterface, IndexingMapOpInterface, LinalgStructuredInterface, MemoryEffectOpInterface, ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
|---|---|
inputs | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
outputs | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
| 결과 | 설명 |
|---|---|
result_tensors | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
linalg.add (linalg::AddOp)두 텐서를 원소별로 더한다.
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이 점을 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예를 들어, linalg.broadcast + linalg.add 시퀀스는 두 피연산자에 대해 다른 어파인 맵을 갖는 linalg.generic으로 낮출 수 있다.
특성(Traits): AttrSizedOperandSegments, RecursiveMemoryEffects, SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>, SingleBlock
인터페이스(Interfaces): ConditionallySpeculatable, DestinationStyleOpInterface, IndexingMapOpInterface, LinalgStructuredInterface, MemoryEffectOpInterface, ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
|---|---|
inputs | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
outputs | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
| 결과 | 설명 |
|---|---|
result_tensors | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
linalg.batch_matmul (linalg::BatchMatmulOp)두 개의 3D 입력에 대한 배치 행렬 곱을 수행.
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
Broadcast와 Transpose 의미는 아래와 같이 명시적 속성 'indexing_maps'를 지정하여 적용할 수 있다.
이것은 리스트 속성이므로, 지정하는 경우 모든 인자에 대한 맵을 포함해야 한다.
Example Transpose:
```mlir
linalg.batch_matmul
indexing_maps = [affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, k, m)>, // transpose
affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, k, n)>,
affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, m, n)>]
ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<2x5x3xf32>,memref<2x5x7xf32>)
outs(%arg2: memref<2x3x7xf32>)
Example Broadcast:
linalg.batch_matmul
indexing_maps = [affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (k)>, // broadcast
affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, k, n)>,
affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, m, n)>]
ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<5xf32>, memref<2x5x7xf32>)
outs(%arg2: memref<2x3x7xf32>)Example Broadcast and Transpose:
linalg.batch_matmul
indexing_maps = [affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (m, k)>, // broadcast
affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, n, k)>, // transpose
affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, m, n)>]
ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<3x5xf32>, memref<2x7x5xf32>)
outs(%arg2: memref<2x3x7xf32>)
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `indexing_maps` | ::mlir::ArrayAttr | AffineMap 배열 속성 |
| `cast` | ::mlir::linalg::TypeFnAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.batch_matvec` (linalg::BatchMatvecOp)
_배치 행렬-벡터 곱 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.batch_mmt4d` (linalg::BatchMmt4DOp)
_두 개의 배치-4D(5D) 입력에 대한 배치 matrix-matrix-transpose 곱 수행._
가장 바깥 배치 차원을 제외하면 의미는 `linalg.batch_matmul`과 동일하며, 비-배치 차원에서의 차이는 `linalg.mmt4d` 대 `linalg.matmul`의 차이와 동일하다. `linalg.mmt4d` 설명을 보라.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.batch_reduce_matmul` (linalg::BatchReduceMatmulOp)
_두 입력에 대한 batch-reduce 행렬 곱 수행. 부분 곱셈 결과는 2D 출력으로 축소된다._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
Broadcast와 Transpose 의미는 아래와 같이 명시적 속성 ‘indexing_maps’를 지정하여 적용할 수 있다. 리스트 속성이므로, 지정하는 경우 모든 인자에 대한 맵을 포함해야 한다.
Example Transpose:
linalg.batch_reduce_matmul indexing_maps = [affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, k, m)>, // transpose affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, k, n)>, affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (m, n)>] ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<2x5x3xf32>,memref<2x5x7xf32>) outs(%arg2: memref<3x7xf32>)
Example Broadcast:
linalg.batch_reduce_matmul indexing_maps = [affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (k)>, // broadcast affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, k, n)>, affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (m, n)>] ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<5xf32>, memref<2x5x7xf32>) outs(%arg2: memref<3x7xf32>)
Example Broadcast and Transpose:
linalg.batch_reduce_matmul indexing_maps = [affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (m, k)>, // broadcast affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, n, k)>, // transpose affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (m, n)>] ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<3x5xf32>, memref<2x7x5xf32>) outs(%arg2: memref<3x7xf32>)
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `indexing_maps` | ::mlir::ArrayAttr | AffineMap 배열 속성 |
| `cast` | ::mlir::linalg::TypeFnAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.batch_vecmat` (linalg::BatchVecmatOp)
_배치 행렬-벡터 곱 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.broadcast` (linalg::BroadcastOp)
_정적 브로드캐스트 연산자_
입력에 `dimensions`를 추가하여 주어진 형태로 브로드캐스트한다.
예:
%bcast = linalg.broadcast ins(%input:tensor<16xf32>) outs(%init:tensor<16x64xf32>) dimensions = [1]
특성(Traits): `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `OpAsmOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `dimensions` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `input` | 임의 타입 값의 memref 또는 ranked tensor |
| `init` | 임의 타입 값의 memref 또는 ranked tensor |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.ceil` (linalg::CeilOp)
_원소별로 ceil(x)를 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.contract` (linalg::ContractOp)
_두 입력을 수축하고, 세 번째에 누적한다._
입력 `A`와 `B`를 `C` 위에 수축하여 출력 `D`를 생성하는 의미는 다음과 같다:
`D[H] = (SUM_{(I ∪ J) \ H} A[I] * B[J]) + C[H]`
여기서 `I`, `J`, `H`는 각 입력/출력에 대한 필수(투영된 순열) `indexing_maps`의 결과에 대응하는 차원 식별자 튜플이다. `SUM_{dims}`는 `dims`에 있는 차원들의 모든 유효 인덱스에 대해 축소함을 의미한다(`I`, `J`, `K`는 차원 식별자의 집합으로 취급).
반복 공간은 `I`, `J`, `H`의 모든 차원(각 `affine_map`의 도메인)으로 구성된다. einsum과 같이, 각 차원의 반복 타입은 추론되며 다음 중 하나이다:
- reduction: 차원이 `A`와 `B`를 인덱싱하는 데 사용되지만 `C`에는 사용되지 않는다. 위 의미에 따라, 이 차원들은 수축(축소)된다.
- parallel: 차원이 `C`와 `A`/`B` 중 최소 하나를 인덱싱하는 데 사용되며, matmul 용어에서 ‘M-유사’(A와 C에 사용), ‘N-유사’(B와 C에 사용), ‘배치’(A, B, C 모두에 사용) 차원으로 구분된다.
예를 들어, batch-matmul은 `I = ⟨ b, m, k ⟩`, `J = ⟨ b, k, n ⟩`, `H = ⟨ b, m, n ⟩`(여기서 `k`는 수축 축소 차원, `m`, `n`, `b`는 병렬)으로 주어지며 다음과 같이 표현된다:
%D = linalg.contract indexing_maps = [affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, m, k)>, affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, k, n)>, affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, m, n)>] ins(%A, %B: tensor<?x?x?xf32>, tensor<?x?x?xf32>) outs(%C: tensor<?x?x?xf32>) -> tensor<?x?x?xf32>
`affine_map` 결과에서 차원을 치환함으로써 입력/출력에 대한 접근을 임의로 전치할 수 있다. 유사하게, 피연산자 어느 한 쪽에서 차원을 생략함으로써 임의의 브로드캐스트도 달성할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 다음은 `A`에 전치를 적용하고 `B`의 2D 행렬을 배치 차원에 따라 브로드캐스트하는 batch-matmul 변형이다:
linalg.contract indexing_maps = [affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, k, m)>, affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (k, n)>, affine_map<(batch, m, n, k) -> (batch, m, n)>] ins(%A, %B: memref<?x?x?xf32>, memref<?x?xf32>) outs(%C: memref<?x?x?xf32>)
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격/절단한다.
TODO: 결합/누적 연산 및 곱셈 연산에 대한 제어 허용.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `indexing_maps` | ::mlir::ArrayAttr | AffineMap 배열 속성 |
| `cast` | ::mlir::linalg::TypeFnAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_1d_ncw_fcw` (linalg::Conv1DNcwFcwOp)
_1-D 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NCW
- 커널: FCW
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_1d_nwc_wcf` (linalg::Conv1DNwcWcfOp)
_1-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_1d` (linalg::Conv1DOp)
_채널 없는 1-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_nchw_fchw` (linalg::Conv2DNchwFchwOp)
_2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NCHW
- 커널: FCHW
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_nchw_fchw_q` (linalg::Conv2DNchwFchwQOp)
_제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NCHW
- 커널: FCHW
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. 이는 양자화 연산에서 흔한 제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_ngchw_fgchw` (linalg::Conv2DNgchwFgchwOp)
_2-D 그룹 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NGCHW
- 커널: FGCHW
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_ngchw_gfchw` (linalg::Conv2DNgchwGfchwOp)
_2-D 그룹 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NGCHW
- 커널: GFCHW
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_ngchw_gfchw_q` (linalg::Conv2DNgchwGfchwQOp)
_제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한 2-D 그룹 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NGCHW
- 커널: GFCHW
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. 이는 양자화 연산에서 흔한 제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_fhwc` (linalg::Conv2DNhwcFhwcOp)
_2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NHWC
- 커널: FHWC
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_fhwc_q` (linalg::Conv2DNhwcFhwcQOp)
_제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NHWC
- 커널: FHWC
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. 이는 양자화 연산에서 흔한 제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_hwcf` (linalg::Conv2DNhwcHwcfOp)
_2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NHWC
- 커널: HWCF
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_nhwc_hwcf_q` (linalg::Conv2DNhwcHwcfQOp)
_제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NHWC
- 커널: HWCF
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. 이는 양자화 연산에서 흔한 제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_nhwgc_gfhwc` (linalg::Conv2DNhwgcGfhwcOp)
_2-D 그룹 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NHWGC
- 커널: GFHWC
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d_nhwgc_gfhwc_q` (linalg::Conv2DNhwgcGfhwcQOp)
_제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한 2-D 그룹 컨볼루션 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NHWGC
- 커널: GFHWC
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. 이는 양자화 연산에서 흔한 제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_2d` (linalg::Conv2DOp)
_채널 없는 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_3d_ncdhw_fcdhw` (linalg::Conv3DNcdhwFcdhwOp)
_3-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_3d_ndhwc_dhwcf` (linalg::Conv3DNdhwcDhwcfOp)
_3-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_3d_ndhwc_dhwcf_q` (linalg::Conv3DNdhwcDhwcfQOp)
_제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한 3-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. 이는 양자화 연산에서 흔한 제로 포인트 오프셋을 포함한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.conv_3d` (linalg::Conv3DOp)
_채널 없는 3-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.copy` (linalg::CopyOp)
_텐서를 원소별로 복사._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `cast` | ::mlir::linalg::TypeFnAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_1d_ncw_cw` (linalg::DepthwiseConv1DNcwCwOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 1-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. multiplier는 1로 설정되며, 대부분의 depthwise 컨볼루션에 대한 특수 케이스이다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_1d_nwc_wc` (linalg::DepthwiseConv1DNwcWcOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 1-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. multiplier는 1로 설정되며, 대부분의 depthwise 컨볼루션에 대한 특수 케이스이다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_1d_nwc_wcm` (linalg::DepthwiseConv1DNwcWcmOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 1-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nchw_chw` (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNchwChwOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. multiplier는 1로 설정되며, 대부분의 depthwise 컨볼루션에 대한 특수 케이스이다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nhwc_hwc` (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNhwcHwcOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. multiplier는 1로 설정되며, 대부분의 depthwise 컨볼루션에 대한 특수 케이스이다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nhwc_hwc_q` (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNhwcHwcQOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nhwc_hwcm` (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNhwcHwcmOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_2d_nhwc_hwcm_q` (linalg::DepthwiseConv2DNhwcHwcmQOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 2-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_3d_ncdhw_cdhw` (linalg::DepthwiseConv3DNcdhwCdhwOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 3-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. multiplier는 1로 설정되며, 대부분의 depthwise 컨볼루션에 대한 특수 케이스이다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_3d_ndhwc_dhwc` (linalg::DepthwiseConv3DNdhwcDhwcOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 3-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. multiplier는 1로 설정되며, 대부분의 depthwise 컨볼루션에 대한 특수 케이스이다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.depthwise_conv_3d_ndhwc_dhwcm` (linalg::DepthwiseConv3DNdhwcDhwcmOp)
_심층(depth-wise) 3-D 컨볼루션 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.div` (linalg::DivOp)
_첫 번째 텐서를 두 번째 텐서로 원소별로 나눈다._
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이를 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예: `linalg.broadcast` + `linalg.div` → 서로 다른 어파인 맵의 `linalg.generic`.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.div_unsigned` (linalg::DivUnsignedOp)
_첫 번째 텐서를 두 번째 텐서로 원소별로 나눈다. 정수 타입에 대해서는 부호 없는 나눗셈을 수행한다._
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이를 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예: `linalg.broadcast` + `linalg.div` → 서로 다른 어파인 맵의 `linalg.generic`.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.dot` (linalg::DotOp)
_두 벡터의 점곱을 계산하여 스칼라 결과를 생성._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.elementwise` (linalg::ElementwiseOp)
_원소별 연산 수행_
`kind` 속성은 수행할 산술 연산을 나타낸다. 연산 종류는 단항(예: max), 이항(예: add), 삼항(예: select)일 수 있다.
기본적으로 모든 인덱싱 맵은 아이덴티티이다. 기본 인덱싱 맵의 경우, 모든 입력과 출력 형태는 일치해야 한다. 각 아이덴티티 맵의 차원 수는 결과 타입의 랭크와 동일하다.
피연산자에 대해 전치 및/또는 브로드캐스트가 필요할 때는 피연산자와 결과에 대한 어파인 맵을 사용자가 제공해야 한다. 맵이 제공되지 않으면 각 피연산자에 대해 기본 아이덴티티 맵이 추론된다.
반복자 타입은 항상 모두 `parallel`이다. 반복자 타입은 내부 구조화 연산 구성에 필요하다.
반복자 타입의 차원 수는 결과 타입의 랭크로부터 추론된다.
예:
기본 인덱싱 맵을 사용하는 단항 linalg.elementwise 정의:
%exp = linalg.elementwise kind=#linalg.elementwise_kind<exp> ins(%x : tensor<4x16x8xf32>) outs(%y: tensor<4x16x8xf32>) -> tensor<4x16x8xf32>
사용자 정의 인덱싱 맵을 사용하는 이항 linalg.elementwise 정의:
%add = linalg.elementwise kind=#linalg.elementwise_kind<add> indexing_maps = [#transpose, #broadcast, #identity] ins(%exp, %arg1 : tensor<4x16x8xf32>, tensor<4x16xf32>) outs(%arg2: tensor<4x8x16xf32>) -> tensor<4x8x16xf32>
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `kind` | ::mlir::linalg::ElementwiseKindAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23 |
| `indexing_maps` | ::mlir::ArrayAttr | AffineMap 배열 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.erf` (linalg::ErfOp)
_원소별로 erf(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.exp` (linalg::ExpOp)
_원소별로 exp(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.fill` (linalg::FillOp)
_출력 텐서를 주어진 값으로 채운다._
임의 랭크 출력 텐서에서 동작한다. 연산은 스칼라 접근만 수행하므로 랭크 다형적이다. 값 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 출력을 동일 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgFillOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.fill_rng_2d` (linalg::FillRng2DOp)
_출력 텐서를 의사 난수로 채운다._
선형 합동 생성기를 이용해 의사 난수를 생성한다. 생성된 난수의 분포에 대한 보장은 없다. 순차적으로 생성하는 대신, 데이터 원소마다 하나의 난수 생성기를 인스턴스화하여 병렬로 실행한다. seed 피연산자와 데이터 원소의 인덱스가 난수 생성을 시드한다. min과 max 피연산자는 난수 범위를 제한한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.floor` (linalg::FloorOp)
_원소별로 floor(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.generic` (linalg::GenericOp)
계산의 핵심 속성을 속성(attribute)로 지정하는 일반 Linalg op 형태.
예쁜(pretty) 형태로 `linalg.generic` op는 다음과 같이 작성된다:
linalg.generic #trait_attribute ins(%A, %B : memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>, memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>) outs(%C : memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>) attrs = {other-optional-attributes} {region}
여기서 #trait_attributes는 다음을 포함하는 사전 속성의 별칭이다:
- doc [옵션]: 문서화 문자열
- indexing_maps: 각 입력/출력 뷰마다 하나의 AffineMapAttr 리스트. 각 AffineMapAttr은 루프와 각 뷰 내 인덱싱 사이의 매핑을 지정한다.
- library_call [옵션]: `linalg.generic` 연산이 매핑되는 외부 라이브러리 함수명을 담은 StringAttr. 외부 라이브러리는 동적 링크된다고 가정하며, 강한 컴파일 타임 보장은 제공되지 않는다. 해당 라이브러리 호출이 없으면, `linalg.generic`은 항상 루프로 낮춰진다.
- iterator_types: 둘러싸는 루프의 타입을 지정하는 ArrayAttr. 각 리스트 원소는 parallel, reduction, window 중 하나의 반복자를 나타낸다.
예: MLIR에서 `#matmul_trait` 속성을 정의하는 방법:
#matmul_accesses = [ (m, n, k) -> (m, k), (m, n, k) -> (k, n), (m, n, k) -> (m, n) ] #matmul_trait = { doc = "C(m, n) += A(m, k) * B(k, n)", indexing_maps = #matmul_accesses, library_call = "linalg_matmul", iterator_types = ["parallel", "parallel", "reduction"] }
그리고 여러 곳에서 재사용할 수 있다:
linalg.generic #matmul_trait ins(%A, %B : memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>, memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>) outs(%C : memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>) {other-optional-attributes} { ^bb0(%a: f32, %b: f32, %c: f32) : %d = arith.mulf %a, %b: f32 %e = arith.addf %c, %d: f32 linalg.yield %e : f32 }
이는 다음 중 하나로 낮춰질 수 있다:
call @linalg_matmul(%A, %B, %C) : (memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>, memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>, memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification>) -> ()
또는 다음과 유사한 IR:
scf.for %m = %c0 to %M step %c1 { scf.for %n = %c0 to %N step %c1 { scf.for %k = %c0 to %K step %c1 { %a = load %A[%m, %k] : memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification> %b = load %B[%k, %n] : memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification> %c = load %C[%m, %n] : memref<?x?xf32, stride_specification> %d = arith.mulf %a, %b: f32 %e = arith.addf %c, %d: f32 store %e, %C[%m, %n] : memref<?x?x?xf32, stride_specification> } } }
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `OpAsmOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `indexing_maps` | ::mlir::ArrayAttr | AffineMap 배열 속성 |
| `iterator_types` | ::mlir::ArrayAttr | 반복자 타입은 enum이어야 한다. |
| `doc` | ::mlir::StringAttr | 문자열 속성 |
| `library_call` | ::mlir::StringAttr | 문자열 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.index` (linalg::IndexOp)
_Linalg index 연산_
구문:
operation ::= linalg.index $dim attr-dict : type($result)
`linalg.index` 연산은 즉시 둘러싼 linalg 구조화 연산의 반복 차원 `dim`의 반복 인덱스를 반환한다. `dim` 속성은 인덱싱 맵 도메인에서 접근되는 차원의 위치를 지정한다.
예:
#map = affine_map<(i, j) -> (i, j)> linalg.generic {indexing_maps = [#map, #map], iterator_types = ["parallel", "parallel"]} outs(%I, %J : memref<?x?xindex>, memref<?x?xindex>) { ^bb0(%arg0 : index, %arg1 : index): // Access the outer iteration dimension i %i = linalg.index 0 : index // Access the inner iteration dimension j %j = linalg.index 1 : index linalg.yield %i, %j : index, index }
이는 다음과 유사한 IR로 낮춰질 수 있다:
%0 = dim %I, %c0 : memref<?x?xindex> %1 = dim %I, %c1 : memref<?x?xindex> scf.for %i = %c0 to %0 step %c1 { scf.for %j = %c0 to %1 step %c1 { store %i, %I[%i, %j] : memref<?x?xindex> store %j, %J[%i, %j] : memref<?x?xindex> } }
특성(Traits): `AlwaysSpeculatableImplTrait`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `InferTypeOpInterface`, `NoMemoryEffect (MemoryEffectOpInterface)`
효과(Effects): `MemoryEffects::Effect{}`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `dim` | ::mlir::IntegerAttr | 최소값 0인 64비트 부호 없는 정수 속성 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | index |
### `linalg.pack` (linalg::PackOp)
_Linalg.pack 연산_
구문:
operation ::= linalg.pack $source
(padding_value ( $padding_value^ : type($padding_value) ))?
(outer_dims_perm = $outer_dims_perm^)?
inner_dims_pos = $inner_dims_pos
inner_tiles =
custom<DynamicIndexList>($inner_tiles, $static_inner_tiles)
into $dest attr-dict : type($source) -> type($dest)
“pack” 연산은 랭크 `n`의 소스 텐서를 랭크 `n + k`의 결과 텐서로 변환한다. 결과는 타일링되고 패킹된 레이아웃(경우에 따라 패딩 포함)을 가지며, 선택적으로 타일링된 소스 텐서 차원을 전치한다.
`inner_tiles`(필수)는 `k`개의 타일 크기를 지정한다. 이 타일 크기들은 동일한 순서로 가장 하위(“inner”) 결과 텐서 차원 크기에 대응한다. 타일 크기는 정적 또는 동적일 수 있다.
`inner_dims_pos`(필수)는 타일링되는 `k`개의 소스 텐서 차원을 지정한다(0 <= k <= n).
- `inner_dims_pos[i]`는 `inner_tiles[i]`에 의해 타일링되는 소스 텐서 차원을 지정한다(0 <= i < k). `inner_dims_pos`의 모든 값은 [0, n) 범위여야 한다.
- 타일링된 차원(크기 `inner_tiles`)은 나타나는 순서대로 결과 텐서의 끝에 추가된다. 즉, `shape(result)[rank(result) + i] = inner_tiles[i]` (0 <= i < k).
- 타일링된 차원에 대해 다음 관계가 성립한다: `shape(result)[inner_dims_pos[i]] = shape(source)[inner_dims_pos[i]] / inner_tiles[i]` (⌈/⌉는 CeilDiv).
예: `inner_tiles = [16, 32]`이면, 결과 텐서의 형태는 `...x16x32`이다. `inner_dims_pos = [0, 1]`이면, 0번째 소스 차원은 16으로 타일링되고 1번째 소스 차원은 32로 타일링된다. 다른 소스 차원(있다면)은 타일링되지 않는다. `inner_dims_pos = [1, 0]`이면 1번째 차원은 16, 0번째 차원은 32로 타일링된다.
예:
// NC to NCnc %0 = linalg.pack %source inner_dims_pos = [0, 1] inner_tiles = [8, 32] into %dest : tensor<128x256xf32> -> tensor<16x8 x 8x32 xf32> // \ / \ / // Outer Dims: 16x8 Inner Dims: 8x32
// CHW to CHWhw %0 = linalg.pack %source inner_dims_pos = [2, 1] inner_tiles = [4, 2] into %dest : tensor<3x20x24xf32> -> tensor<3x10x6 x 4x2 xf32> // \ / \ / // Outer Dims: 3x10x6 Inner Dims: 4x2
// HCW to HCWhw %0 = linalg.pack %source inner_dims_pos = [2, 0] inner_tiles = [4, 2] into %dest : tensor<18x3x32xf32> -> tensor<9x3x8 x 4x2 xf32> // \ / \ / // Outer Dims: 9x3x8 Inner Dims: 4x2
`outer_dims_perm`(옵션)은 바깥 차원에 대한 순열을 지정한다. 지정하는 경우 `n`개 원소를 가져야 한다.
예:
// CK to KCck %0 = linalg.pack %source outer_dims_perm = [1, 0] inner_dims_pos = [0, 1] inner_tiles = [8, 32] into %dest : tensor<128x256xf32> -> tensor<8x16 x 8x32 xf32> // \ / // compare with "NC to NCnc": outer dims are transposed
`padding_value`는 완전하게 나누어 떨어지지 않는 차원의 경계에서 패딩 값을 지정한다. 패딩은 선택 사항이다:
- 생략된 경우, 모든 inner 타일에 대해 `shape(source)[inner_dims_pos[i]] % inner_tiles[i] == 0`이라고 가정한다. 즉, 모든 inner 타일이 결과 텐서의 해당 바깥 차원을 완전히 나눈다. 완전히 나누어 떨어지지 않으면 UB이다.
- 지정된 경우, 타일을 완성하기 위해 상위 차원(high)으로 패딩한다. linalg.pack에 필요하지 않은 인위적 패딩(각 패킹된 차원마다 마지막 타일을 완성하는 데 필요한 것 이상)은 허용되지 않는다. 추가 패딩이 요청되면 UB이다. 동적 형태에서는 요구사항을 정적으로 검증할 수 없으므로 UB로 취급된다.
예:
%0 = linalg.pack %arg0 padding_value(%pad : f32) outer_dims_perm = [2, 1, 0]
inner_dims_pos = [1] inner_tiles = [2] into %arg1
: tensor<200x127x256xf32> -> tensor<256x64x200x2xf32>
//
// padded and tiled dim
//
// Source dimension 1 is tiled. 64 does not divide 127 evenly, so 1 padded
// element is added at the end.
//
// Note: Only tiled dimensions can be padded.
인위적 패딩이 있는 잘못된 예:
%0 = linalg.pack %src padding_value(%cst : f32) inner_dims_pos = [0]
inner_tiles = [8] into %dest
: tensor<9xf32> -> tensor<3x8xf32>
//
// expect tensor<2x8xf32> because CeilDiv(9, 8) = 2
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `InferTypeOpInterface`, `LinalgRelayoutOpInterface`, `NoMemoryEffect (MemoryEffectOpInterface)`, `OpAsmOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
효과(Effects): `MemoryEffects::Effect{}`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `outer_dims_perm` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
| `inner_dims_pos` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
| `static_inner_tiles` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `source` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor |
| `dest` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor |
| `padding_value` | 임의 타입 |
| `inner_tiles` | index 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor |
### `linalg.softmax` (linalg::SoftmaxOp)
_Softmax 연산자_
구문:
operation ::= linalg.softmax attr-dict
dimension ( $dimension )
ins ( $input : type($input) )
outs ( $output : type($output) )
(-> type($result)^)?
linalg.softmax는 수치적으로 안정적인 softmax를 계산한다.
주어진 입력 텐서와 지정된 차원 `d`에 대해 다음을 계산한다:
1. 차원 `d`를 따라 최대값 `m`
2. f(x) = exp(x - m)
3. 차원 `d`를 따라 f(x)의 합 l(x)
4. 최종 결과 f(x) / l(x)
이는 구조화 연산의 작은 DAG로 더 낮춰지는 집약(aggregate) linalg 연산이다.
경고: 타일링 기능과 관련하여, 구현은 제공된 차원이 의미에 부합하는지 확인하지 않는다. 변환을 호출하는 쪽이 softmax 의미에 맞는 크기를 각 차원에 대해 제공하도록 책임이 있다.
인터페이스(Interfaces): `AggregatedOpInterface`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`, `TilingInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `dimension` | ::mlir::IntegerAttr | 64비트 부호 없는 정수 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `input` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped |
| `output` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.unpack` (linalg::UnPackOp)
_Linalg.unpack 연산_
구문:
operation ::= linalg.unpack $source
(outer_dims_perm = $outer_dims_perm^)?
inner_dims_pos = $inner_dims_pos
inner_tiles =
custom<DynamicIndexList>($inner_tiles, $static_inner_tiles)
into $dest attr-dict : type($source) -> type($dest)
“unpack” 연산은 타일링되고 패킹된 레이아웃을 가진 랭크 `n`의 소스 텐서를 랭크 `n - k`의 결과 텐서로 변환한다.
`inner_tiles`(필수)는 `k`개의 타일 크기를 지정한다. 이 타일 크기들은 가장 하위(“inner”) 소스 텐서 차원 크기에 대응한다. 다음과 같은 경우 이 연산의 동작은 정의되지 않는다:
- `inner_tiles`가 해당 소스 텐서 차원 크기와 정확히 일치하지 않는 경우
- 또는, `inner_dims_pos[i]` 차원의 크기가 `inner_tiles[i]`로 정확히 나누어 떨어지지 않는 경우(`outer_dims_perm`이 지정되지 않았다고 가정)
`inner_dims_pos`(필수)는 패킹된 소스 텐서를 만들기 위해 `inner_tiles`로 타일링되었던 `k`개의 결과(언패킹된) 텐서 차원을 지정한다. 소스(패킹된) 텐서 차원은 다음과 같이 언패킹될 수 있다.
- `0 <= i < k`에 대해, `shape(result)[inner_dims_pos[i]] <= shape(source)[n-k+i] * shape(source)[inner_dims_pos[i]]`
- `0 <= j < n-k`이고 `j`가 `inner_dims_pos`에 포함되지 않는 경우, `shape(result)[j] = shape(source)[j]`
`outer_dims_perm`(옵션)은 바깥 차원에 대한 순열을 지정한다. 지정하는 경우 `n - k`개 원소를 가져야 한다. 지정한 경우, 어떤 차원을 결합하기 전에 이 순열이 적용된다.
참고: 언팩 연산은 패킹 연산이 도입한 패딩을 제거할 수 있으므로, `NumElementsOf(source) >= NumElementsOf(result)`가 성립한다.
예:
// NCnc to NC: %0 = linalg.unpack %source inner_dims_pos = [0, 1] inner_tiles = [8, 32] into %dest : tensor<16x8 x 8x32 xf32> -> tensor<128x256xf32> // \ / \ / // Outer Dims: 16x8 Inner Dims: 8x32
// CK to KCck: %0 = linalg.unpack %source outer_dims_perm = [1, 0] inner_dims_pos = [0, 1] inner_tiles = [8, 32] into %dest : tensor<8x16 x 8x32 xf32> -> tensor<128x256xf32> // \ / \ / // Outer Dims: 8x16 Inner Dims: 8x32
// CHW to CHWhw: %0 = linalg.unpack %source inner_dims_pos = [2, 1] inner_tiles = [4, 2] into %dest : tensor<3x10x6 x 4x2 xf32> -> tensor<3x20x24xf32> // \ / \ / // Outer Dims: 3x10x6 Inner Dims: 4x2
// HCW to HCWhw %0 = linalg.unpack %source inner_dims_pos = [2, 0] inner_tiles = [4, 2] into %dest : tensor<9x3x8 x 4x2 xf32> -> tensor<18x3x32xf32> // \ / \ / // Outer Dims: 9x3x8 Inner Dims: 4x2
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `InferTypeOpInterface`, `LinalgRelayoutOpInterface`, `NoMemoryEffect (MemoryEffectOpInterface)`, `OpAsmOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
효과(Effects): `MemoryEffects::Effect{}`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `outer_dims_perm` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
| `inner_dims_pos` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
| `static_inner_tiles` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `source` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor |
| `dest` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor |
| `inner_tiles` | index 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor |
### `linalg.winograd_filter_transform` (linalg::WinogradFilterTransformOp)
_Winograd 필터 변환 연산자_
구문:
operation ::= linalg.winograd_filter_transform attr-dict
fmr ( $fmr )
ins ( $filter : type($filter) )
outs ( $output : type($output) )
-> type($result)
Winograd Conv2D 알고리즘은 linalg Conv2D 연산자를 배치 행렬 곱으로 변환한다. 행렬 곱 이전에, 필터와 입력을 배치 행렬 곱에 적합한 형식으로 변환한다. 행렬 곱 이후에는 출력을 최종 결과 텐서로 변환한다.
알고리즘 F(m x m, r x r)는 다음과 같다:
Y = A^T x [(G x g x G^T) @ (B^T x d x B)] x A
출력 Y의 크기는 m x m. 필터 g의 크기는 r x r. 입력 d의 크기는 (m + r - 1) x (m + r - 1). A^T, A, G^T, G, B^T, B는 변환 행렬이다.
이 연산자는 Winograd Conv2D 알고리즘에서 필터 변환(G x g x G^T)의 상위 개념을 표현하기 위해 정의된다.
인터페이스(Interfaces): `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `TilingInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `fmr` | mlir::linalg::WinogradConv2DFmrAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1, 2 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `filter` | 임의 타입 값의 4D 텐서 |
| `output` | 임의 타입 값의 4D 텐서 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 4D 텐서 |
### `linalg.winograd_input_transform` (linalg::WinogradInputTransformOp)
_Winograd 입력 변환 연산자_
구문:
operation ::= linalg.winograd_input_transform attr-dict
fmr ( $fmr )
ins ( $input : type($input) )
outs ( $output : type($output) )
-> type($result)
Winograd Conv2D 알고리즘은 linalg Conv2D 연산자를 배치 행렬 곱으로 변환한다. 행렬 곱 이전에, 필터와 입력을 배치 행렬 곱에 적합한 형식으로 변환한다. 행렬 곱 이후에는 출력을 최종 결과 텐서로 변환한다.
알고리즘 F(m x m, r x r)는 다음과 같다:
Y = A^T x [(G x g x G^T) @ (B^T x d x B)] x A
출력 Y의 크기는 m x m. 필터 g의 크기는 r x r. 입력 d의 크기는 (m + r - 1) x (m + r - 1). A^T, A, G^T, G, B^T, B는 변환 행렬이다.
이 연산자는 Winograd Conv2D 알고리즘에서 입력 변환(B^T x d x B)의 상위 개념을 표현하기 위해 정의된다.
인터페이스(Interfaces): `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `TilingInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `fmr` | mlir::linalg::WinogradConv2DFmrAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1, 2 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `input` | 임의 타입 값의 4D 텐서 |
| `output` | 임의 타입 값의 6D 텐서 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 6D 텐서 |
### `linalg.winograd_output_transform` (linalg::WinogradOutputTransformOp)
_Winograd 출력 변환 연산자_
구문:
operation ::= linalg.winograd_output_transform attr-dict
fmr ( $fmr )
ins ( $value : type($value) )
outs ( $output : type($output) )
-> type($result)
Winograd Conv2D 알고리즘은 linalg Conv2D 연산자를 배치 행렬 곱으로 변환한다. 행렬 곱 이전에, 필터와 입력을 배치 행렬 곱에 적합한 형식으로 변환한다. 행렬 곱 이후에는 출력을 최종 결과 텐서로 변환한다.
알고리즘 F(m x m, r x r)는 다음과 같다:
Y = A^T x [(G x g x G^T) @ (B^T x d x B)] x A
출력 Y의 크기는 m x m. 필터 g의 크기는 r x r. 입력 d의 크기는 (m + r - 1) x (m + r - 1). A^T, A, G^T, G, B^T, B는 변환 행렬이다.
이 연산자는 Winograd Conv2D 알고리즘에서 출력 변환(A^T x y x A)의 상위 개념을 표현하기 위해 정의된다.
인터페이스(Interfaces): `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `TilingInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `fmr` | mlir::linalg::WinogradConv2DFmrAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1, 2 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `value` | 임의 타입 값의 6D 텐서 |
| `output` | 임의 타입 값의 4D 텐서 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 4D 텐서 |
### `linalg.yield` (linalg::YieldOp)
_Linalg yield 연산_
`linalg.yield`는 `linalg` generic 연산 내 리전의 블록에 대한 특수 종결자(terminator) 연산이다. 이는 즉시 둘러싼 `linalg` generic 연산으로 값을 반환한다.
예:
linalg.yield %f0, %f1 : f32, f32
특성(Traits): `AlwaysSpeculatableImplTrait`, `ReturnLike`, `Terminator`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `NoMemoryEffect (MemoryEffectOpInterface)`, `RegionBranchTerminatorOpInterface`
효과(Effects): `MemoryEffects::Effect{}`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `values` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.log` (linalg::LogOp)
_원소별로 log(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.map` (linalg::MapOp)
_원소별 연산_
텐서에 대한 원소별 연산을 해당 원소에 대한 산술 연산으로 모델링한다.
예:
%add = linalg.map ins(%lhs, %rhs : tensor<64xf32>, tensor<64xf32>) outs(%init: tensor<64xf32>) (%lhs_elem: f32, %rhs_elem: f32) { %0 = arith.addf %lhs_elem, %rhs_elem: f32 linalg.yield %0: f32 }
짧은 인쇄(shortened) 형태는 바디가 정확히 두 개의 연산(페이로드 연산과 yield)으로 구성되고, 페이로드 연산의 피연산자 수가 블록 인자 수와 같고, 피연산자가 순서대로 블록 인자와 일치하며, yield 피연산자가 페이로드 연산의 결과일 때 사용 가능하다.
위 예시는 짧은 형태로 다음과 같이 출력된다:
%add = linalg.map { arith.addf } ins(%lhs, %rhs : tensor<64xf32>, tensor<64xf32>) outs(%init: tensor<64xf32>)
특성(Traits): `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `OpAsmOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입 값의 memref 또는 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
| `init` | 임의 타입 값의 memref 또는 ranked tensor |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.matmul` (linalg::MatmulOp)
_브로드캐스트나 전치 없이 두 개의 2D 입력에 대한 행렬 곱을 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
브로드캐스트와 전치 의미는 아래와 같이 명시적 속성 ‘indexing_maps’를 지정하여 적용할 수 있다. 리스트 속성이므로, 지정하는 경우 모든 맵을 포함해야 한다.
Example Transpose:
linalg.matmul indexing_maps = [affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (k, m)>, // transpose affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (k, n)>, affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (m, n)>] ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<5x3xf32>,memref<5x7xf32>) outs(%arg2: memref<3x7xf32>)
Example Broadcast:
linalg.matmul indexing_maps = [affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (k)>, // broadcast affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (k, n)>, affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (m, n)>] ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<3xf32>, memref<5x7xf32>) outs(%arg2: memref<3x7xf32>)
Example Broadcast and transpose:
linalg.matmul indexing_maps = [affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (k, m)>, // transpose affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (k)>, // broadcast affine_map<(m, n, k) -> (m, n)>] ins(%arg0, %arg1 : memref<5x3xf32>, memref<7xf32>) outs(%arg2: memref<3x7xf32>)
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `indexing_maps` | ::mlir::ArrayAttr | AffineMap 배열 속성 |
| `cast` | ::mlir::linalg::TypeFnAttr | 허용되는 32비트 부호 없는 정수 케이스: 0, 1 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.matvec` (linalg::MatvecOp)
_행렬-벡터 곱 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.max` (linalg::MaxOp)
_두 입력 간의 최대값(부호 있는)을 원소별로 취한다._
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이를 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예: `linalg.broadcast` + `linalg.max` → 서로 다른 어파인 맵의 `linalg.generic`.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.min` (linalg::MinOp)
_두 입력 간의 최소값(부호 있는)을 원소별로 취한다._
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이를 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예: `linalg.broadcast` + `linalg.min` → 서로 다른 어파인 맵의 `linalg.generic`.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.mmt4d` (linalg::Mmt4DOp)
_두 4D 입력에 대한 matrix-matrix-transpose 곱 수행._
`linalg.matmul`과의 차이점:
- 오른쪽 피연산자가 전치되어 있으며, 이름의 ‘t’는 transpose를 의미한다.
- 입력/출력 텐서는 2D 모양 대신 4D 모양을 갖는다. 이는 하나의 2D 타일 분할 수준을 갖춘 2D 행렬로 해석되며, 이로 인해 2+2=4 차원을 갖는다. inner 타일 차원은 아래에서 ‘0’ 접미사로 구분된다. 예: LHS 행렬 형태 (M, K, M0, K0)는 MxK 타일, 각 타일의 형태 M0xK0을 의미한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.mul` (linalg::MulOp)
_두 텐서를 원소별로 곱한다._
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이를 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예: `linalg.broadcast` + `linalg.mul` → 서로 다른 어파인 맵의 `linalg.generic`.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.negf` (linalg::NegFOp)
_원소별로 negf(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nchw_max` (linalg::PoolingNchwMaxOp)
_최대 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nchw_sum` (linalg::PoolingNchwSumOp)
_합(sum) 풀링 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NCHW
- 커널: HW
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_ncw_max` (linalg::PoolingNcwMaxOp)
_최대 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_ncw_sum` (linalg::PoolingNcwSumOp)
_합(sum) 풀링 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NCW
- 커널: W
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_ndhwc_max` (linalg::PoolingNdhwcMaxOp)
_3D 최대 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_ndhwc_min` (linalg::PoolingNdhwcMinOp)
_3D 최소 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_ndhwc_sum` (linalg::PoolingNdhwcSumOp)
_3D 합(sum) 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [3]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nhwc_max` (linalg::PoolingNhwcMaxOp)
_최대 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nhwc_max_unsigned` (linalg::PoolingNhwcMaxUnsignedOp)
_부호 없는 최대 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nhwc_min` (linalg::PoolingNhwcMinOp)
_최소 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nhwc_min_unsigned` (linalg::PoolingNhwcMinUnsignedOp)
_부호 없는 최소 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nhwc_sum` (linalg::PoolingNhwcSumOp)
_합(sum) 풀링 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NHWC
- 커널: HW
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [2]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nwc_max` (linalg::PoolingNwcMaxOp)
_최대 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nwc_max_unsigned` (linalg::PoolingNwcMaxUnsignedOp)
_부호 없는 최대 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nwc_min` (linalg::PoolingNwcMinOp)
_최소 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nwc_min_unsigned` (linalg::PoolingNwcMinUnsignedOp)
_부호 없는 최소 풀링 수행._
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.pooling_nwc_sum` (linalg::PoolingNwcSumOp)
_합(sum) 풀링 수행._
레이아웃:
- 입력: NWC
- 커널: W
입력 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgConvolutionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `strides` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
| `dilations` | ::mlir::DenseIntElementsAttr | 형태 [1]의 64비트 부호 없는 정수 요소 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.powf` (linalg::PowFOp)
_두 입력에 대해 원소별로 powf(lhs, rhs)를 적용한다. powf(arg, 2)는 `linalg.square`를 사용하라._
부동소수점 값에만 적용된다.
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이를 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예: `linalg.broadcast` + `linalg.powf` → 서로 다른 어파인 맵의 `linalg.generic`.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.quantized_batch_matmul` (linalg::QuantizedBatchMatmulOp)
_두 3D 입력에 대한 배치 행렬 곱 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. 양자화 변형은 행렬 곱의 좌/우 피연산자에 대한 제로 포인트 조정을 포함한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.quantized_matmul` (linalg::QuantizedMatmulOp)
_두 2D 입력에 대한 행렬 곱 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다. 양자화 변형은 행렬 곱의 좌/우 피연산자에 대한 제로 포인트 조정을 포함한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.reciprocal` (linalg::ReciprocalOp)
_원소별로 reciprocal(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.reduce` (linalg::ReduceOp)
_축소(reduce) 연산자_
`inputs`의 `dimensions`에 대해 `combiner`를 실행하고 축소된 결과를 반환한다. `dimensions` 속성은 증가 순으로 축소 차원을 나열해야 한다.
예:
%reduce = linalg.reduce ins(%input:tensor<16x32x64xf32>) outs(%init:tensor<16x64xf32>) dimensions = [1] (%in: f32, %out: f32) { %0 = arith.addf %out, %in: f32 linalg.yield %0: f32 }
짧은 인쇄 형태는 바디가 정확히 두 개의 연산(페이로드와 yield)으로 구성되고, 페이로드 연산의 피연산자 수가 블록 인자 수와 같으며, 첫 번째 블록 인자(init)가 페이로드 연산의 마지막 피연산자이고, 나머지 피연산자/블록 인자가 순서대로 일치하며, yield 피연산자가 페이로드 결과일 때 사용 가능하다.
위 예시는 짧은 형태로 다음과 같이 출력된다:
%reduce = linalg.reduce { arith.addf } ins(%input:tensor<16x32x64xf32>) outs(%init:tensor<16x64xf32>) dimensions = [1]
특성(Traits): `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SameVariadicOperandSize`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `OpAsmOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `dimensions` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | 증가 순이어야 하는 i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입 값의 memref 또는 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
| `inits` | 임의 타입 값의 memref 또는 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| «unnamed» | 임의 타입 값의 tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.round` (linalg::RoundOp)
_원소별로 round(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.rsqrt` (linalg::RsqrtOp)
_원소별로 rsqrt(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.select` (linalg::SelectOp)
_첫 번째 피연산자로 제공되는 이진 조건에 따라 값을 선택한다._
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이를 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예: `linalg.broadcast` + `linalg.select` → 서로 다른 어파인 맵의 `linalg.generic`.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.sqrt` (linalg::SqrtOp)
_원소별로 sqrt(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.square` (linalg::SquareOp)
_원소별로 square(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.sub` (linalg::SubOp)
_두 텐서를 원소별로 뺀다._
모양과 원소 타입은 동일해야 한다. 적절한 캐스트, 브로드캐스트, 축소는 이 연산을 호출하기 전에 수행되어야 한다.
이는 축소/브로드캐스트/원소 캐스트 의미가 명시적임을 뜻한다. 이후 패스는 이를 고려해 낮추기를 수행할 수 있다. 예: `linalg.broadcast` + `linalg.sub` → 서로 다른 어파인 맵의 `linalg.generic`.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.tanh` (linalg::TanhOp)
_원소별로 tanh(x) 적용._
입력 피연산자에 대한 수치 캐스팅은 수행되지 않는다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.transpose` (linalg::TransposeOp)
_전치 연산자_
`permutation`에 따라 `input`의 차원을 치환한다. `dim(result, i) = dim(input, permutation[i])`
이 연산은 실제로 데이터를 이동한다. 이는 단지 전치된 “뷰”만을 생성하는 메타데이터 연산인 `memref.transpose`와는 다르다.
예:
%transpose = linalg.transpose ins(%input:tensor<16x64xf32>) outs(%init:tensor<64x16xf32>) permutation = [1, 0]
특성(Traits): `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `OpAsmOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 속성(Attributes):
| 속성 | MLIR 타입 | 설명 |
| --- | --- | --- |
| `permutation` | ::mlir::DenseI64ArrayAttr | i64 조밀 배열 속성 |
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `input` | 임의 타입 값의 memref 또는 ranked tensor |
| `init` | 임의 타입 값의 memref 또는 ranked tensor |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result` | 임의 타입 값의 tensor 가변 개수 |
### `linalg.vecmat` (linalg::VecmatOp)
_벡터-행렬 곱 수행._
내부 곱셈의 피연산자에 대해 수치 캐스팅을 수행하여, 누산기/출력과 동일한 데이터 타입으로 승격한다.
특성(Traits): `AttrSizedOperandSegments`, `RecursiveMemoryEffects`, `SingleBlockImplicitTerminator<YieldOp>`, `SingleBlock`
인터페이스(Interfaces): `ConditionallySpeculatable`, `DestinationStyleOpInterface`, `IndexingMapOpInterface`, `LinalgContractionOpInterface`, `LinalgStructuredInterface`, `MemoryEffectOpInterface`, `ReifyRankedShapedTypeOpInterface`
#### 피연산자(Operands):
| 피연산자 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `inputs` | 임의 타입의 가변 개수 |
| `outputs` | 임의 타입 값의 shaped 가변 개수 |
#### 결과(Results):
| 결과 | 설명 |
| --- | --- |
| `result_tensors` | 임의 타입 값의 ranked tensor 가변 개수 |
'linalg' 다이얼렉트 문서 링크
-----------------------------
- Linalg OpDSL: https://mlir.llvm.org/docs/Dialects/Linalg/OpDSL/